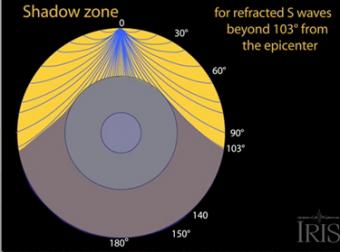
S Wave Shadow Zone Definition

5 A Cross Section Of The Earth With Earthquake Wave Paths Defined And Download Scientific Diagram
Q Tbn 3aand9gcr1nwnmuzsryr1twdfncnufvijunync Ypxkq Usqp Cau

Seismic Study Of Earth S Interior Learning Geology
Seimic Waves And Earth S Interior

S Waves Definition Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
Seismic Wave Wikipedia
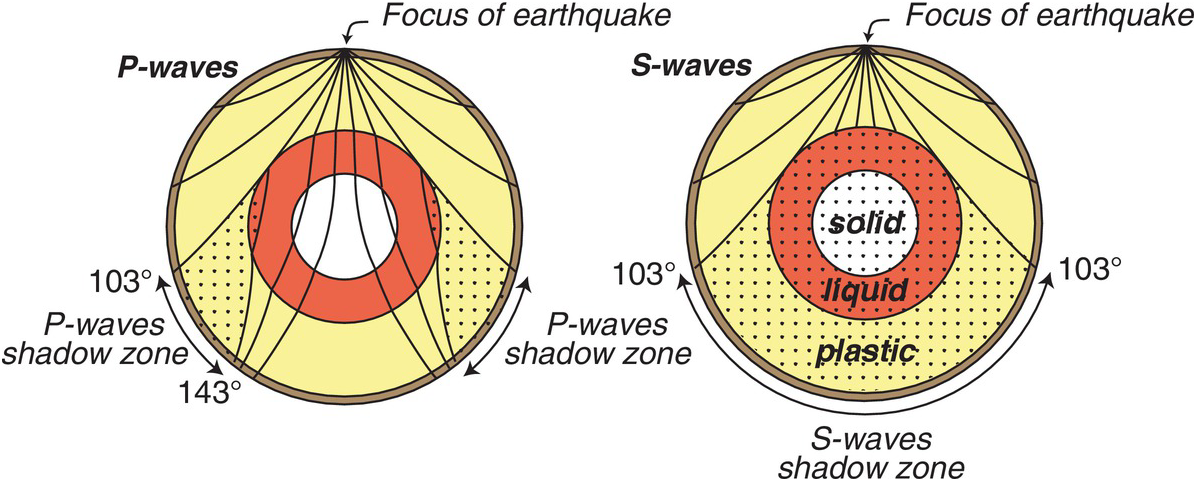
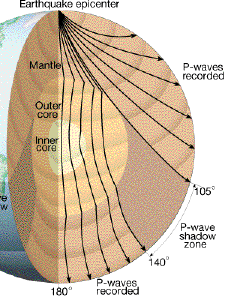
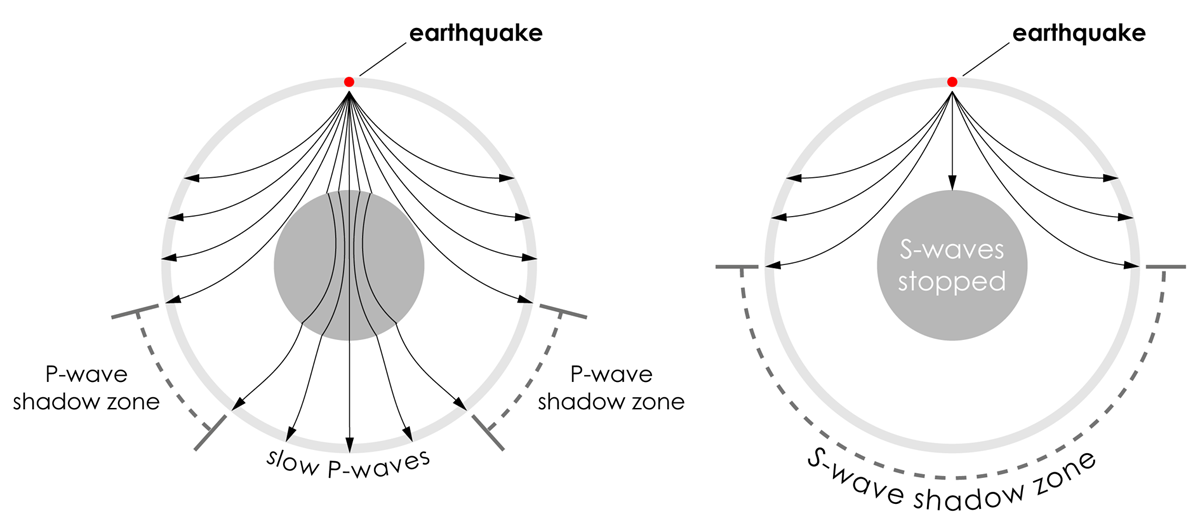
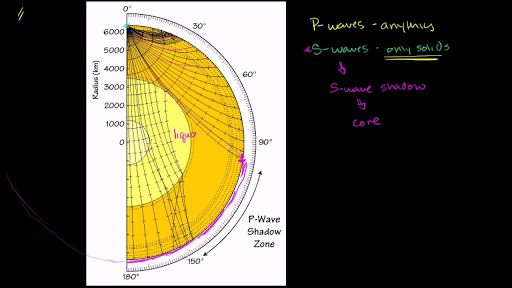
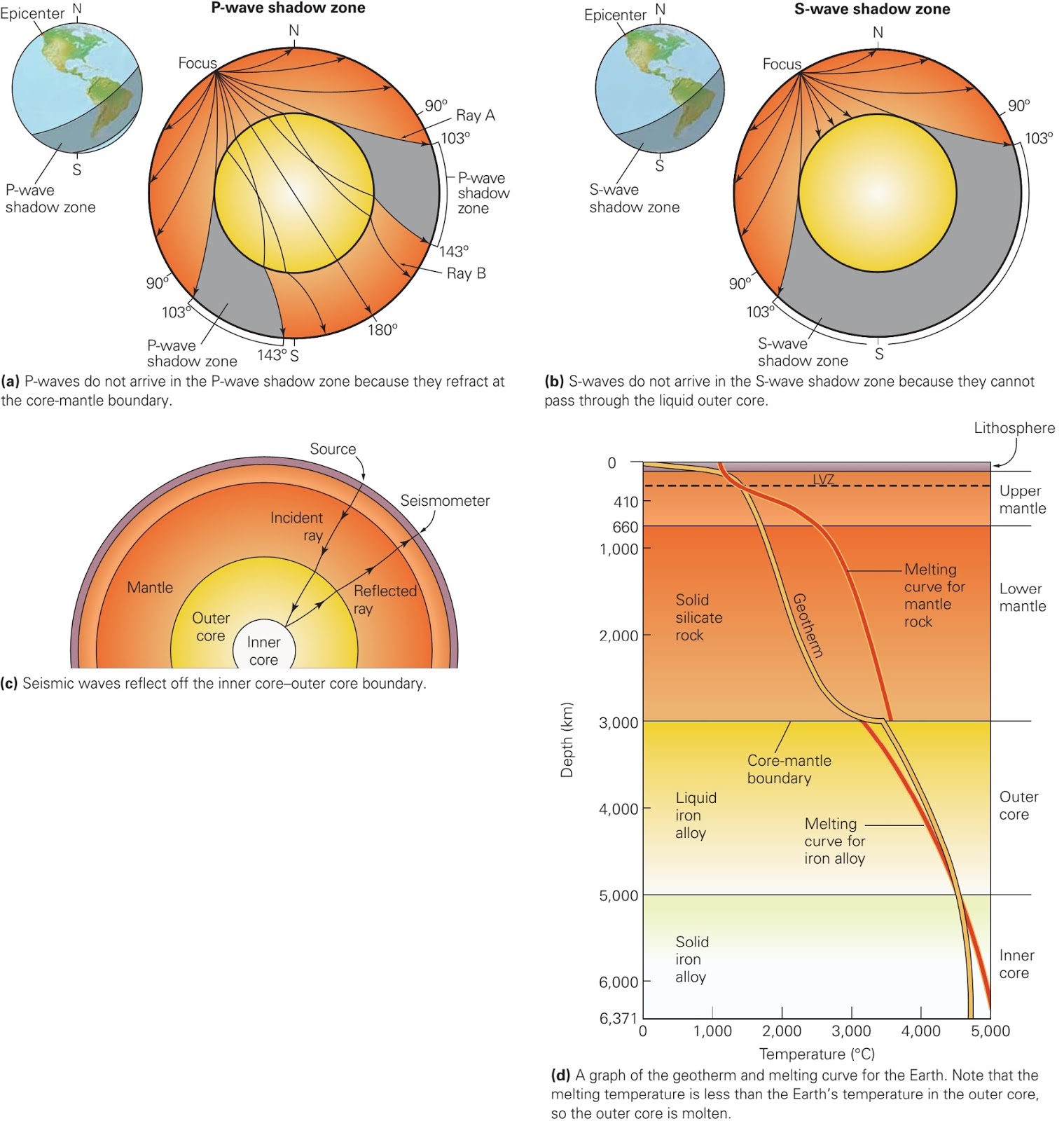
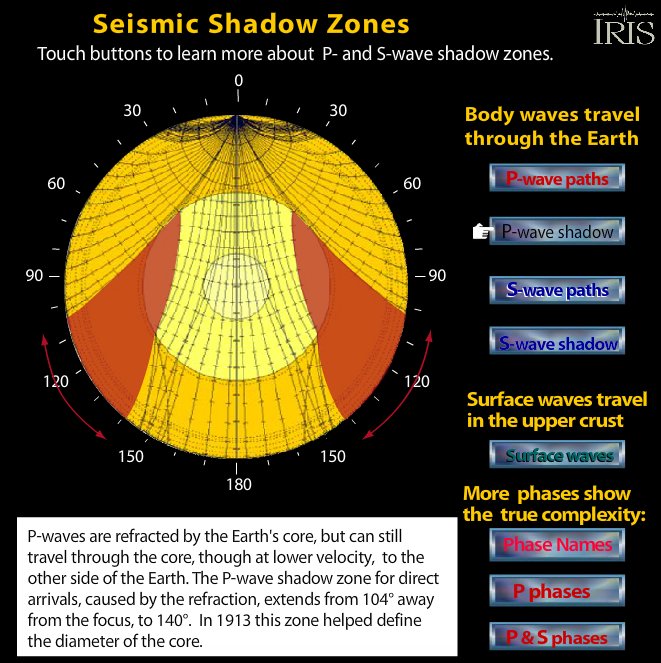
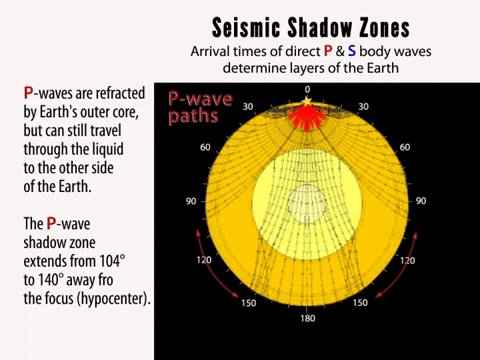
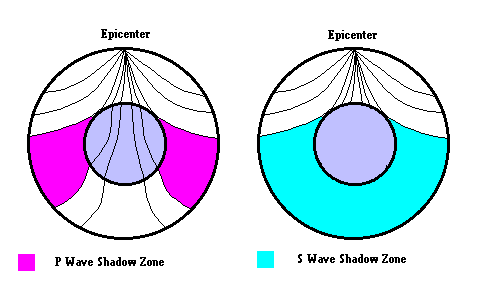
The shadow zone of a P-wave.
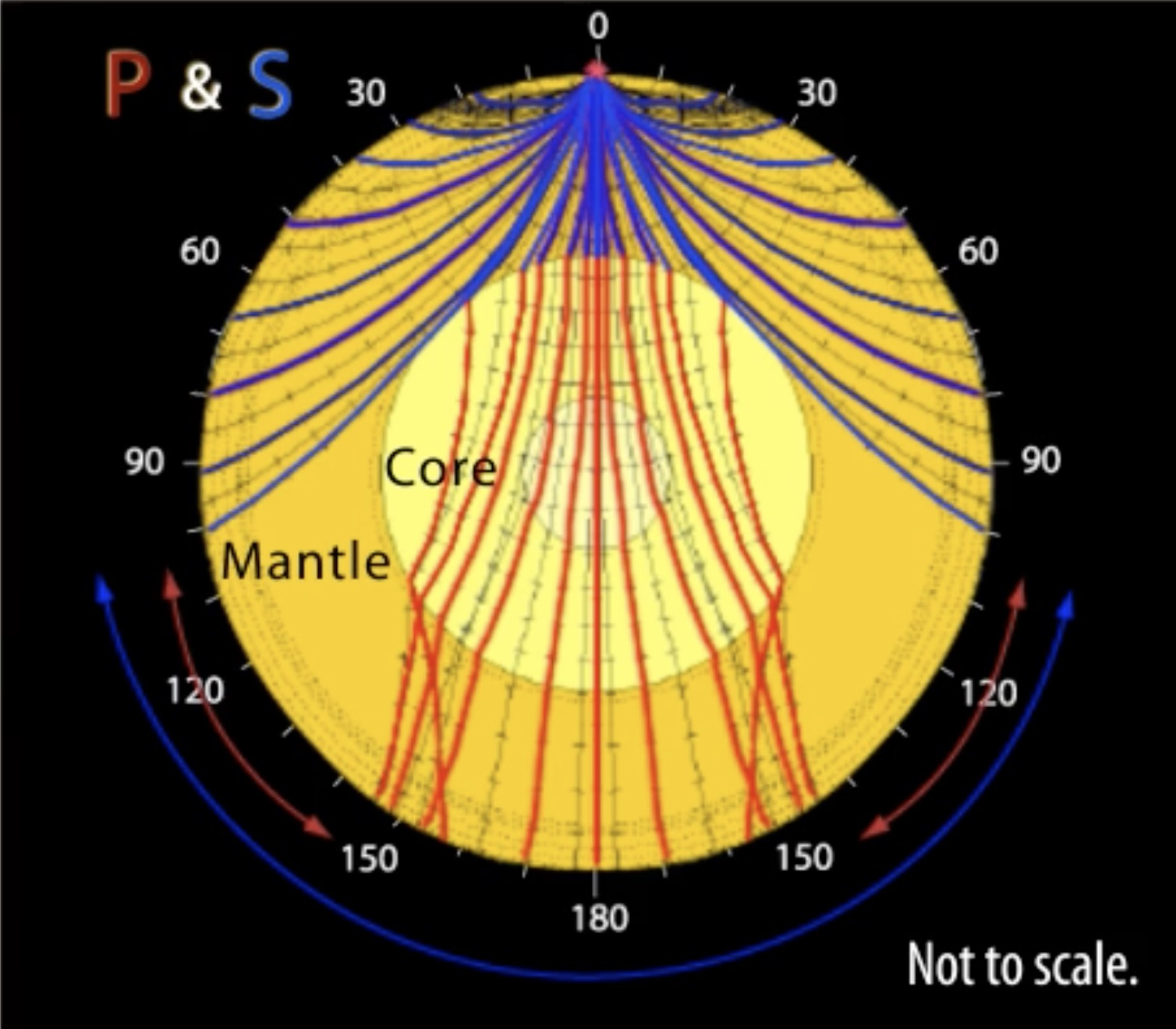
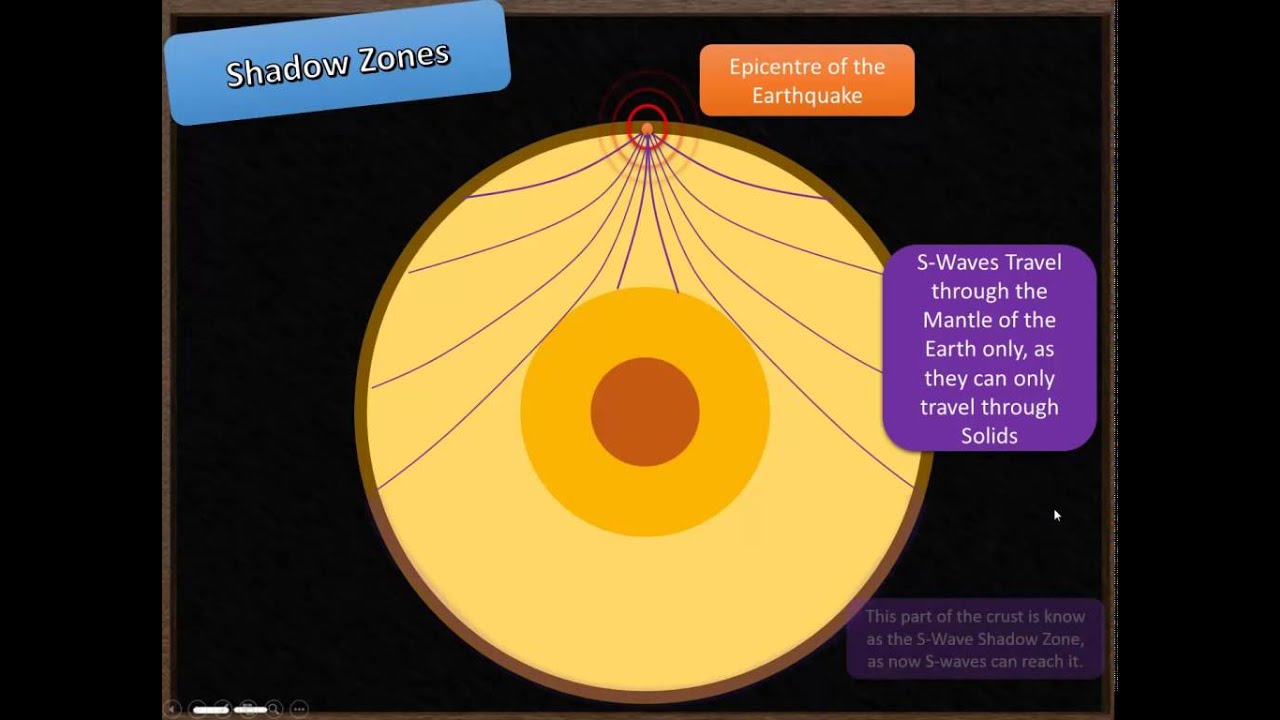
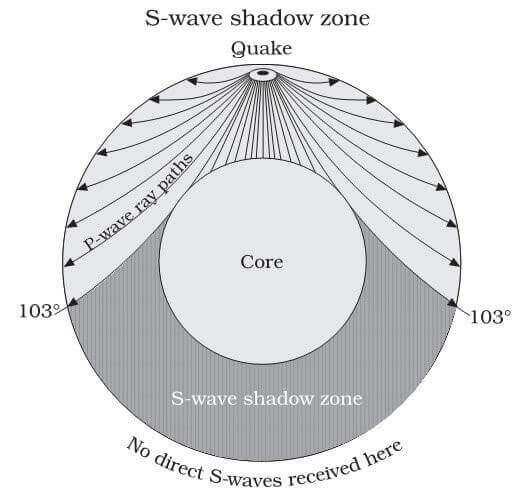
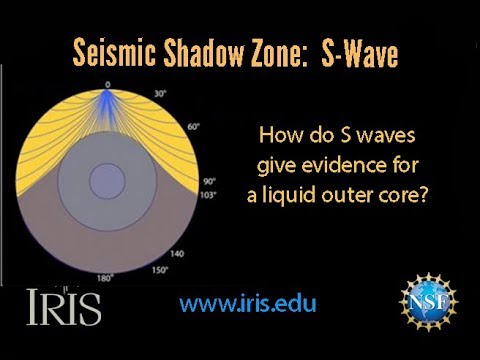
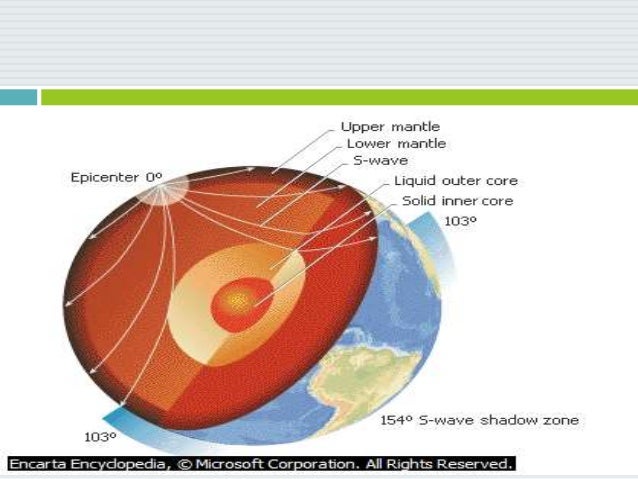
S wave shadow zone definition. The eighth stage for Shadow the Hedgehog and Rouge the Bat;. The entire zone beyond 103° does not receive S-waves, and hence this zone is identified as the shadow zone of S-waves. A solid rocky (silica-rich) shell that extends to a depth of about 2900 km (1800 miles).
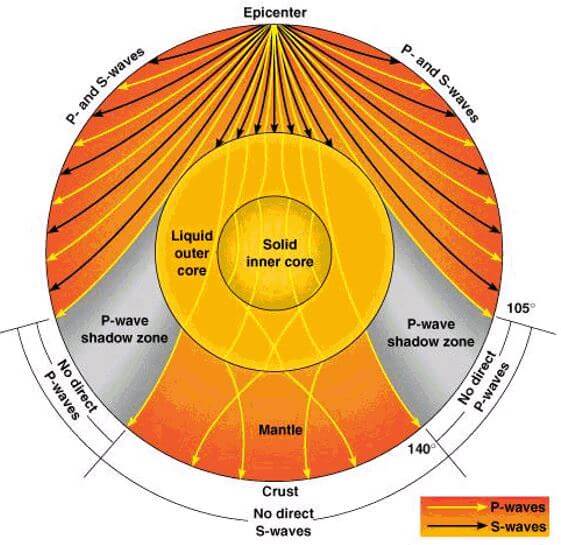
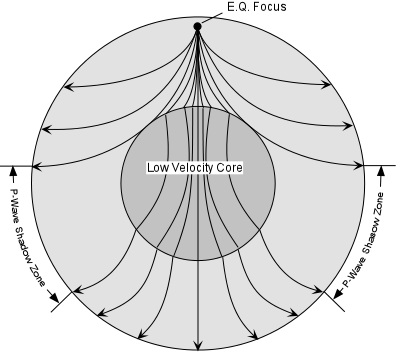
The shadow zone results from S waves being stopped entirely by the liquid core and P waves being bent (refracted) by the liquid core. Let’s say a stack is emitting sound wave meters above the ground. In this case only a refracted wave from the lower half space is observed.
Internal waves at tidal. Low velocity zoneSpecial case:. S-waves do not travel through liquids (they are attenuated).
Analyses based on global climate models forecast bleaching will become an annual event for most of the world’s coral reefs within 30–50 yr. Sound w's longitudinal waves of mechanical energy that transmit the vibrations interpreted as sound (def. The function of the seismic waves is similar to the function of the light and water waves.
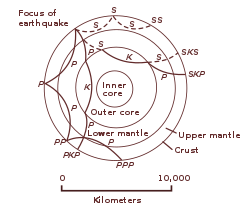
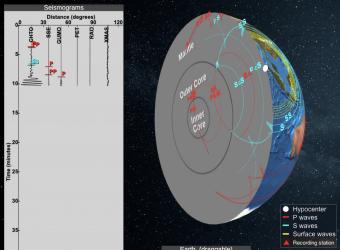
When earthquakes occur, they produce primary and secondary waves (called compression and shear waves sometimes). Your browser does not support the video tag. This observation led to the discovery of the liquid outer core.
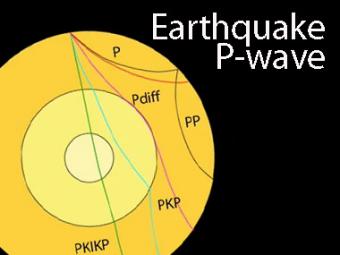
This shows how P waves travel through so. A zone between 105° and 145° from the epicenter was recognized as the shadow zone for both the wave types. Upper portion is ultramafic rock peridotite.
S wave definition is - a wave (as from an earthquake) in which the propagated disturbance is a shear in an elastic medium (such as the earth). See also P-wave shadow zone. This shadow zone has led geologists to a model of the Earth with a solid mantle.
Diffraction of electromagnetic waves. Epicenter of an earthquake. However, during the night is a different story.
Other articles where Shadow zone is discussed:. An S wave is a transverse wave and travels slower than a P wave, thus arriving after the P wave. The one exception is in polar regions where pycnocline.
Waves longer than 2.5 cm and shorter than 5 cm are in an indeterminate zone between capillary and gravity waves. • P- Waves have less shadow zone in compare to S- waves. S-waves are similar to the sine waves we have seen;.
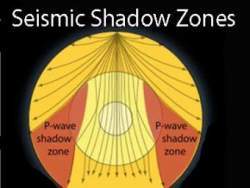
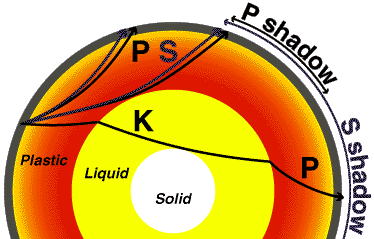
Shadowzones are produced on the other sides of the planet due to waves being refracted or blocked by the liquid outer core of Earth. Why is there a P-wave shadow zone?. The waves can be so powerful they will reach all parts of the Earth and cause it to vibrate like a turning fork.
Convection in the outer core coupled with the rotation of the Earth may create the Earth's Magnetic Field. S wave shadow zone showed that outer core is liquid o Seismological data is also used to study smaller scale features below the Earth’s surface Widely used in oil and gas exploration Seismic reflection profile of a sedimentary basin ° Temperature increases with increasing depth in the earth 15-50 C/km ° Sources of Earth’s heat:. Secondary waves, or S-waves, are seismic waves produced by an earthquake.
By virtue of the fact that the speed that acoustic waves travel at depends on the properties of the medium (i.e. Pycnocline, in oceanography, boundary separating two liquid layers of different densities. See also P-wave shadow zon e.
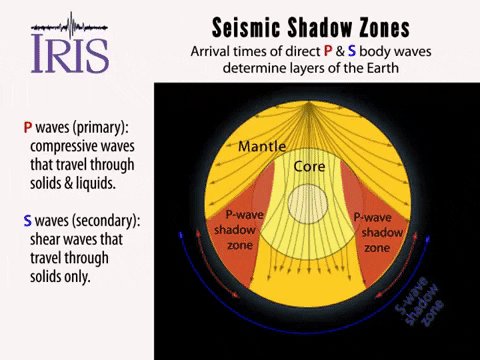
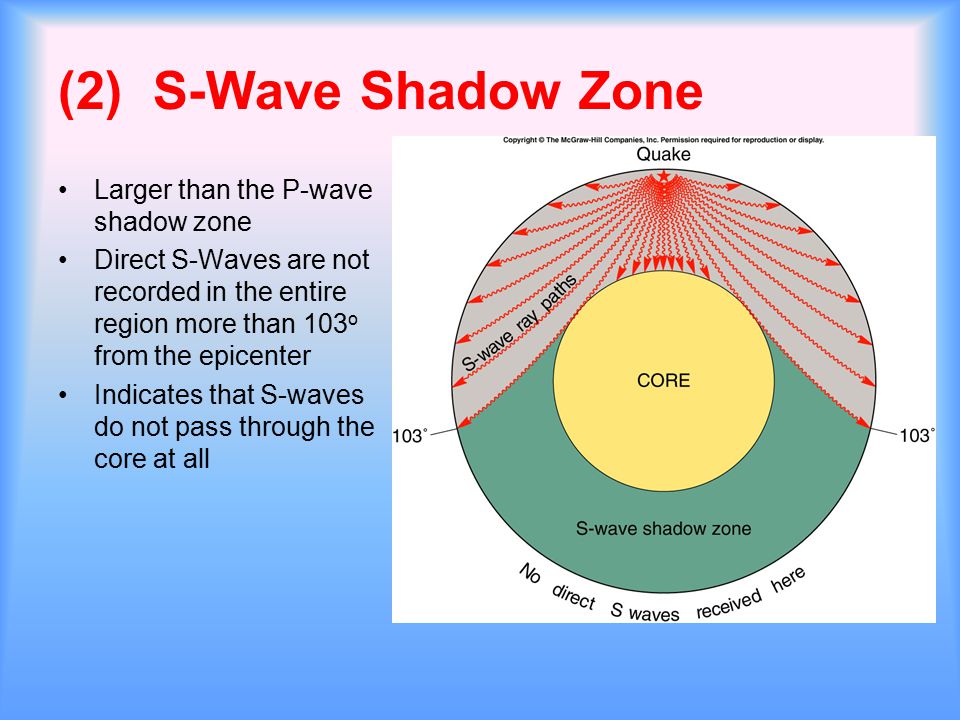
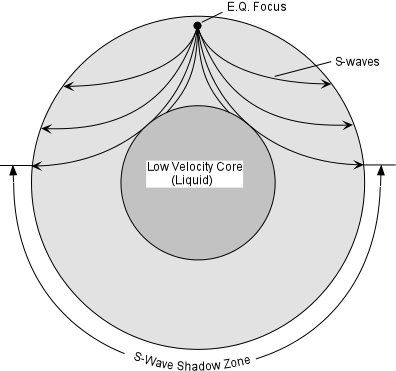
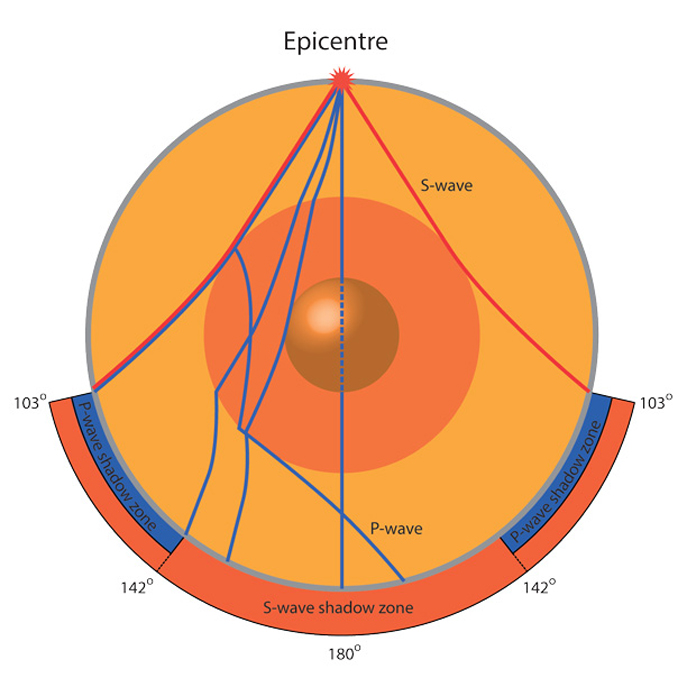
Www.iris.edu/earthquake for more animations. If you live near the sea, have a look at waves on a windy day. The region within an arc of 154° directly opposite an earthquake's epicenter that is marked by the absence of S waves.
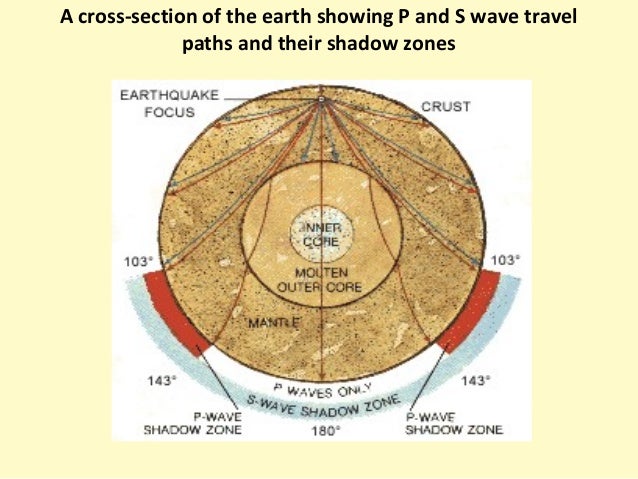
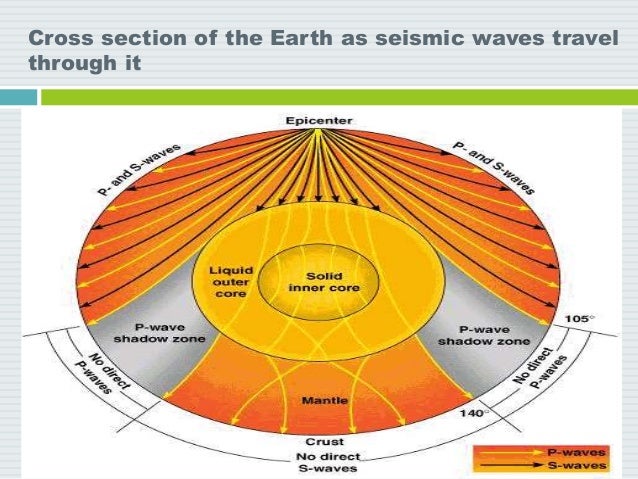
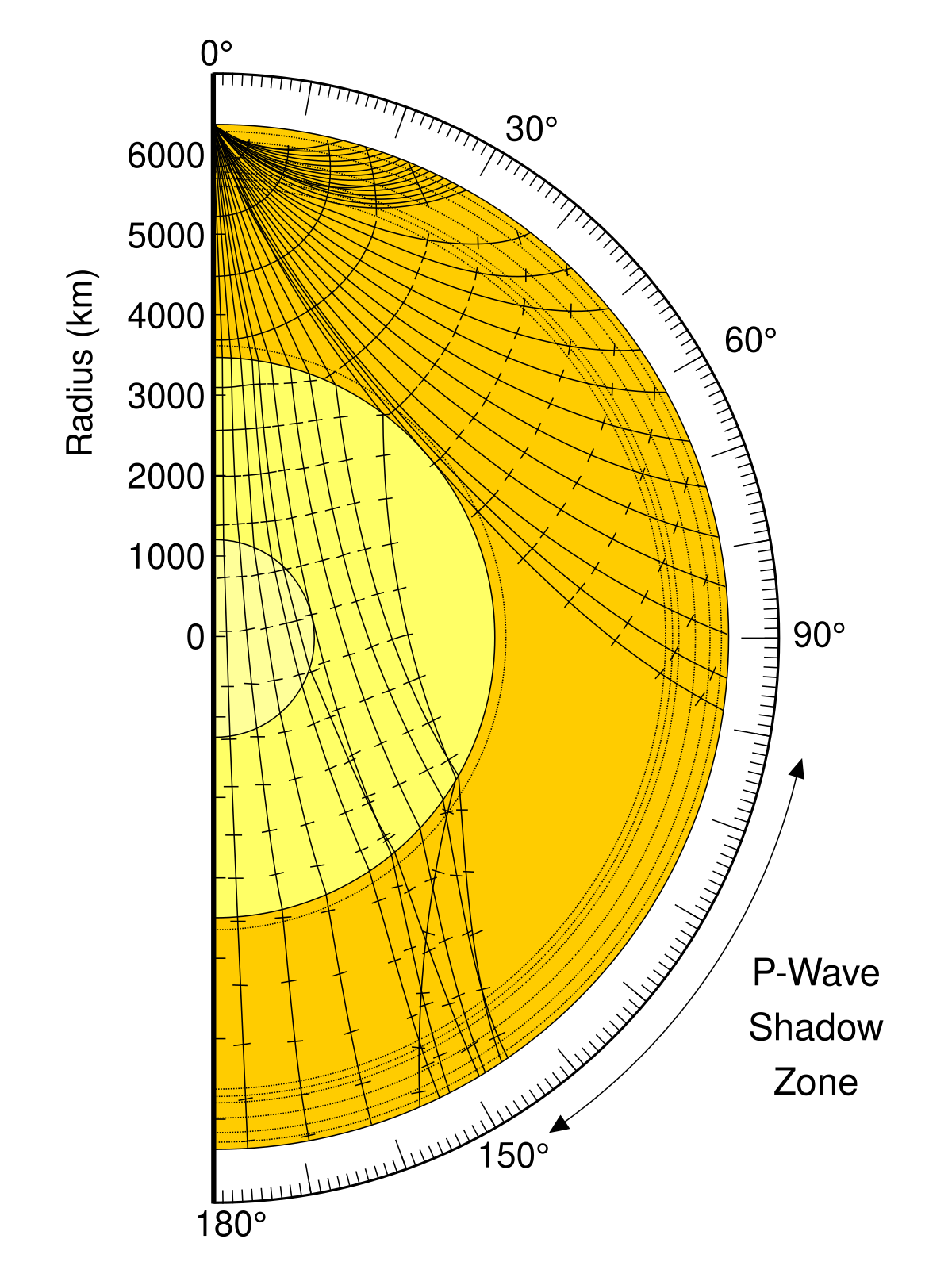
No P-waves are picked up at seismographs 104o to 140o from the earthquakes focus. The result is a P-wave shadow zone. The S-wave shadow zone is due to the fact that S waves can not penetrate the liquid outer core.
Shadow definition is - the dark figure cast upon a surface by a body intercepting the rays from a source of light. It might be outdated or ideologically biased. Outer Core - S waves are not propagated through the outer core - creates an S wave shadow zone.
The S wave shadow zone is the area of the Earth’s surface where S waves are not detected following an earthquake. A zone over the Earth's surface in which P-waves and/or. Communities located many kilometers away will here this noise.
S wave definition, a transverse earthquake wave that travels through the interior of the earth and is usually the second conspicuous wave to reach a seismograph. Noise barriers alongside roads reduce the traffic sound for houses in the shadow zone. Sea water), the propagation of sonar will be complicated.
The S waves are the second wave to reach a seismic station measuring a disturbance. S-waves move in an up and down motion perpendicular to the direction of. S waves can only travel through solids, and as a result do not travel through the liquid core of.
The entire zone beyond 105° does not receive S-waves. The bending, called diffraction. The region that extends from 103º to 143º from the epicenter of an earthquake and is marked by the absence of P waves.The P-wave shadow zone is due to the refraction of seismic waves in the liquid outer core.See also S-wave shadow zone.
S-waves don't penetrate the outer core, so they're shadowed everywhere more than 104° away from the epicenter (from USGS). This animation addresses 3 common variations of S-type seismic body waves. The S-wave shadow zone is a angle past 105 degrees, measured from the focus, that the S waves cannot exceed because they cannot travel through the Earth's liquid region core.
Body wave definition, a transverse or longitudinal earthquake wave that travels through the interior of the earth (distinguished from surface wave). Low velocity zone What happens if we have a low-velocity zone?. He interpreted the acceleration of seismic waves observed within Earth's outer shell as a compositional change within the Earth.
P waves are slowed down (recall equations from previous chapter) which creates a P wave shadow zone. Acoustic shadow zones are exploited by acoustical engineers to reduce noise. Primary waves or P-waves are.
Diffraction of electromagnetic waves. USGS Earthquake Hazards Program, responsible for monitoring, reporting, and researching earthquakes and earthquake hazards. For example, if a wave was traveling to the right, the movement of the ground would be up and down.
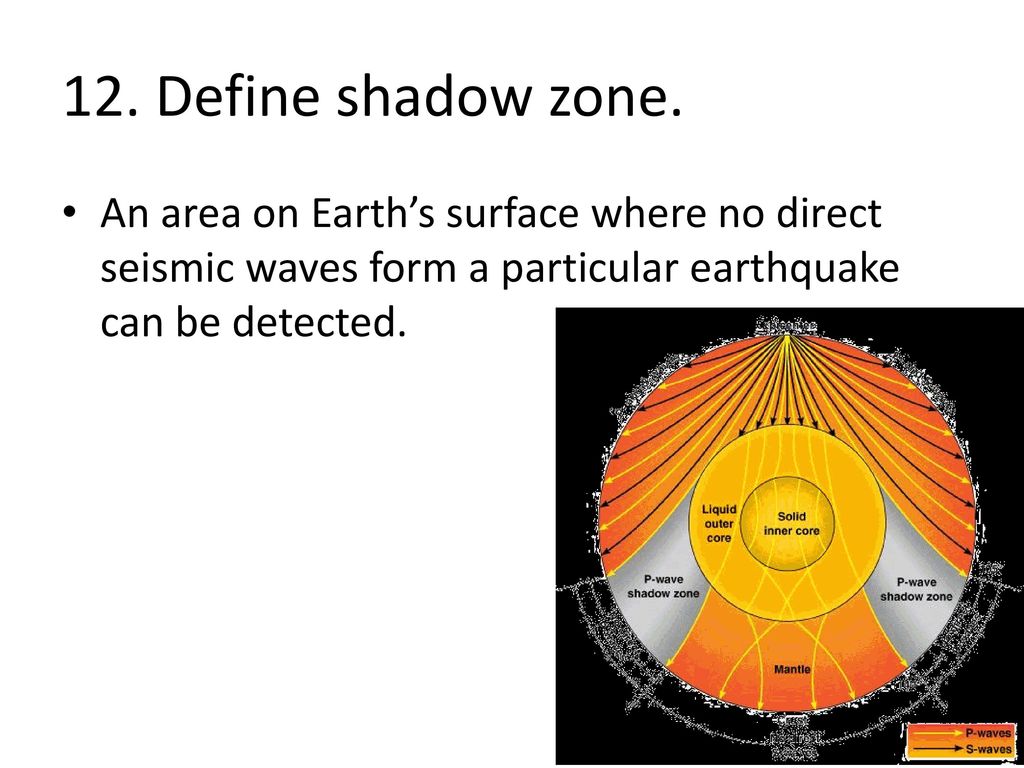
A seismic shadow zone is an area of the Earth's surface where seismographs cannot detect an earthquake after its seismic waves have passed through the Earth. The sound waves from these sources will ultimate refract upward. How to use shadow in a sentence.
Refraction of Sound the bending of sound rays in a nonuniform medium, such as the atmosphere or the ocean, in which the speed of sound depends on the coordinates. The shadow zone of S-wave is larger than that of the P-waves. In oceans a large density difference between surface waters (or upper 100 metres 330 feet) and deep ocean water effectively prevents vertical currents;.
The 35 degree belt around the world where p-waves diminish and eventually die out completely about 105 degree from an earthquake. Wave Ocean is the beach side resort just outside Soleanna’s capital city and an Action Stage that appears in Sonic the Hedgehog.It is the first stage for Sonic the Hedgehog and Miles "Tails" Prower;. In fact, S-waves travel at 60% of the speed of P-waves.
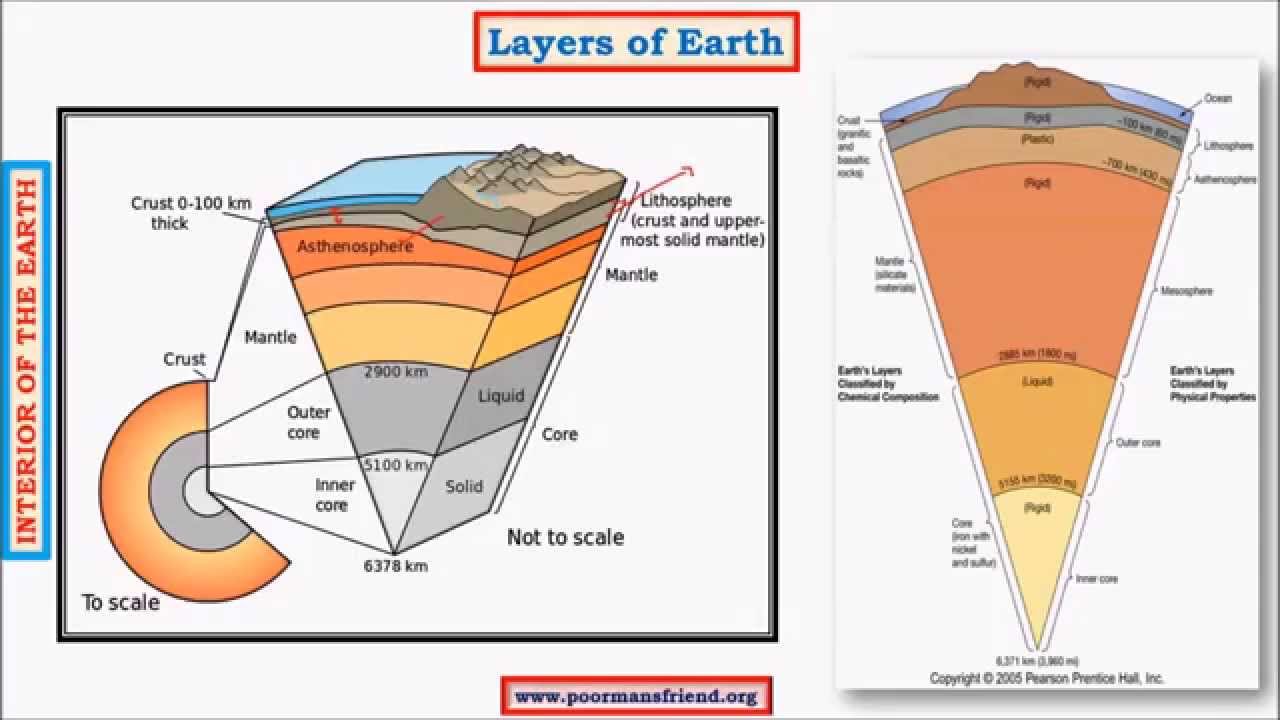
The factor of 10 and a unit conversion into km is absorbed in the definition of the absorption coefficient, a b/100. There is a region of the Earth that will receive no seismic waves form this earthquake due to the S-waves being absorbed by the liquid outer core and the P- waves being curved or refracted by the changing densities of the Earths's interior Shadow Zone (receives no seismic waves) YOU MIGHT ALSO LIKE. Consists of an iron and nickel melt.
A seismic shadow zone is an area of the Earth 's surface where seismographs can only barely detect an earthquake after its seismic waves have passed through the Earth. Match the term on the left with its definition on the right. It is a favored.
• P- Waves act like sound waves. S wave shadow zone The shadow zone results from S waves being stopped entirely by the liquid core. Earthquake waves DO NOT originate at the epicenter.
Three different S-wave phases show how the initial S wave is stopped (damped), or how it changes when encountering boundaries in the Earth. Then no head wave exists on the interface between the first and second layer. What is a P-wave shadow zone?.
Sound rays always turn toward the layer where the speed of sound is lower. A really good example of diffraction can be seen with another type of wave barrier – a harbour or dock wall. Rayleigh waves and Love waves are confined to the _____.
Sonic w's audible sound waves. Or at least two feet if no depth number is specified. P-wave shadow zone Definition :.
The shadow zone is the area of the earth from angular distances of 104 to 140 degrees from a given earthquake that does not receive any direct P waves. As one side of a fault slips past the other, the pressure that had been stored is released and travels radially away from. Seismology and the Earth’s Deep Interior Body Waves and Ray Theory Special case:.
The acceleration must be caused by a higher density material being present at depth. These waves will be refracted right onto the community. The following article is from The Great Soviet Encyclopedia (1979).
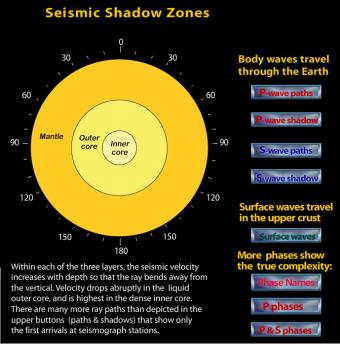
A seismic shadow zone is an area that receives only one type of seismic wave or, in some places, no seismic activity. Seismic shadow zone a. The shadow zone of P-waves appears as a band around the earth between 103° and 142° away from the epicentre.
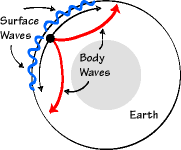
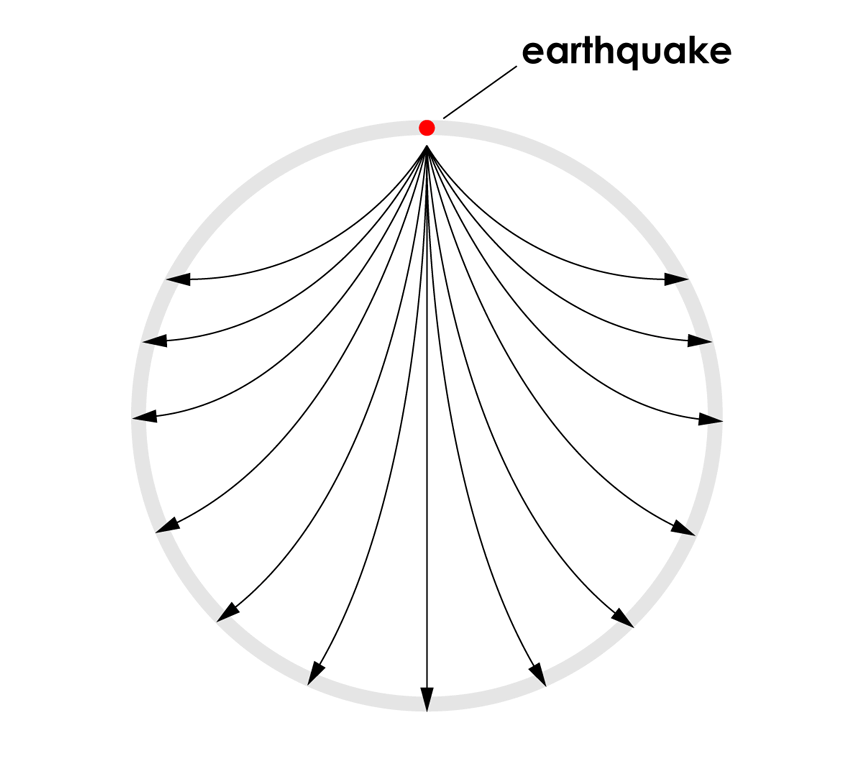
Observations show ocean temperatures are rising due to climate change, resulting in a fivefold increase in the incidence of regional-scale coral bleaching events since the 1980s;. All are shear waves that travel in all directions away from the epicenter of an earthquake. There are two main types of seismic waves:.
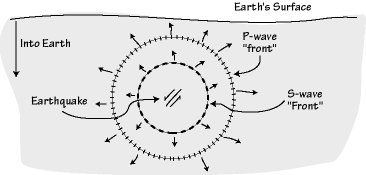
% of Earth's volume. S-waves can only travel through solids. Directly above the focus on the Earth's surface is the earthquake epicenter.
A region of the subsurface from which seismic reflections cannot be detected because their ray-paths do not emerge to the surface. Refraction also produces shadow zones that sound waves do not penetrate because of their curvature. S-wave shadow zone The region within an arc of 1540 directly opposite an earthquake's epicenter that is marked by the absence of S waves.
A radio wave that meets an obstacle has a natural tendency to bend around the obstacle as illustrated in the figure. Mohorovicic realized that the velocity of a seismic wave is related to the density of the material that it is moving through. S- waves ( Secondary waves) The wave created after the reflection of primary waves called S waves (secondary waves).
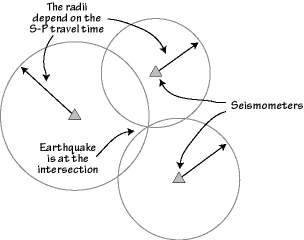
A process used to determine the epicenter of an earthquake 5. A surface wave that causes horizontal motion 6. Earthquake waves start at the focus and travel outward in all directions.
When an earthquake occurs, seismic waves radiate out spherically from the earthquake's focus. S wave a downward deflection of the QRS complex following the R wave in the normal surface electrocardiogram. The shadow zone of P-waves appears as a band around the earth between 105° and 145° away from the epicenter.
Secondary waves (also called S-waves) are about half as fast as P-waves, traveling at about 3.5 km (2 miles) per second, and arrive second at seismographs. In AO Zones, all new construction and substantial improvements of residential structures shall have the lowest floor including basement elevated above the highest adjacent grade at least as high as the depth number specified in feet on the community's Flood Insurance Rate Map (FIRM);. This is called the shadow zone.
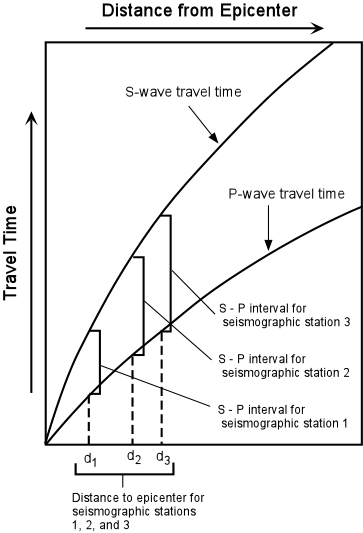
P waves travel faster than S waves, and are the first waves recorded by a seismograph in the event of a disturbance. P waves travel at speeds between 1 and 14 km per second, while S waves travel significantly slower, between 1 and 8 km per second. Seismic shadow zones have taught us much about the inside of the earth.
And the third stage for Silver the Hedgehog (although he does not go through this stage himself, Blaze the Cat does instead). The displacement is perpendicular (or 90 degrees) to the movement of the wave.
Seismic Shadow Zone Basic Introduction Incorporated Research Institutions For Seismology
The Earth And Moon System A Question And Answer Guide To Astronomy

Seismic Shadow Zone Definition Overview Study Com

P Wave Wikipedia

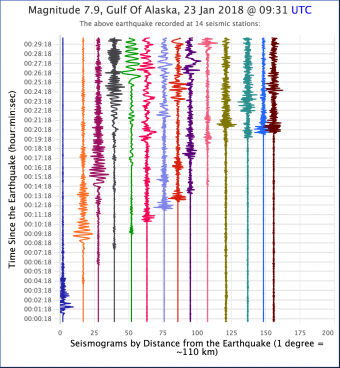
How Do I Read A Seismogram
What Is A Shadow Zone During An Earthquake Quora

Earthquakes Earth S Interior

Earth S Interior Earth Science
Q Tbn 3aand9gcslbmpw0rc86ua3kpto6v30ghiiqpj4ffat9vigqtx4rxhgpg Usqp Cau
Thread By Iris Epo Seismic Shadow Zone How Do P S Waves Give Evidence For A Liquid Outer Core Thread Iris Edu Hq Inclass Ani Earthquake Seismology Data

How Do I Read A Seismogram

Geol212 Planetary Geology

Ncert Notes Earthquake Body Waves Causes Effects

Earthquakes And The Earth S Internal Structure Amnh

Seismology Wikipedia

Compare Contrast Connect Seismic Waves And Determining Earth S Structure Manoa Hawaii Edu Exploringourfluidearth

Thread By Iris Epo Seismic Shadow Zone How Do P S Waves Give Evidence For A Liquid Outer Core Thread Iris Edu Hq Inclass Ani Earthquake Seismology Data
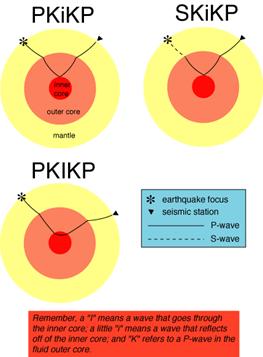
Details Of The Core Not Well Established And Still Open To Revision See Recent Paper By Price On Fe In The Core

Seismic Shadow Zone Definition Overview Study Com

Determination Of Earth Structure Sciencedirect

Seismic Waves Generated By Earthquakes Examined Britannica

Details Of The Core Not Well Established And Still Open To Revision See Recent Paper By Price On Fe In The Core
Seismic Waves P S And Surface Incorporated Research Institutions For Seismology
Seismic Waves
Multiple Choice
Study Of An Earthquake

Details Of The Core Not Well Established And Still Open To Revision See Recent Paper By Price On Fe In The Core
Handout 1 Standard 2 1 A B And C Ppt Download
Seismic Shadow Zones S Wave Shadow Zone Incorporated Research Institutions For Seismology

Upsc Geography Earthquake Neostencil
Earth Structure Earth Science Visionlearning

Evidence For Earth S Layers 8th Grade Science
Seimic Waves And Earth S Interior
Earthquakes
Geophysical Properties Ppt Video Online Download
How Do We Really Know What S Inside The Earth Imaging Earth S Interior With Seismic Waves Incorporated Research Institutions For Seismology
Http Geoscience Msc Sa Edu Au Library 2 1 earths crust and interior Pdf

Quiz Worksheet Seismic Shadow Zone Study Com

Seismic Waves Shadow Zone Of P Waves And S Waves Pmf Ias

Src Qk Html
Seimic Waves And Earth S Interior
Earth Structure Earth Science Visionlearning
Earthquakes
P1 Earthquake Shadow Zones Youtube

Seismic Study Of Earth S Interior Learning Geology
What Is A Shadow Zone During An Earthquake Quora

L O Swbat Describe The Shadow Zones Ppt Download
1

How Are Earthquake Magnitudes Measured The Seismogram A Typical Seismogram Ppt Download
Seimic Waves And Earth S Interior
Http Geoscience Msc Sa Edu Au Library 2 1 earths crust and interior Pdf
Seismic Shadow Zone Basic Introduction Incorporated Research Institutions For Seismology
The Earth S Interior
How We Know About The Earth S Core Video Khan Academy
Q Tbn 3aand9gcryxf7fjvwx59zdwcx6dbvp5olw6i2ddsvwfi49viy7rbsltrsu Usqp Cau
Seismic Shadow Zones S Wave Shadow Zone Incorporated Research Institutions For Seismology

Earth S Interior
G4 Earth S Interior Upsc Ias Shadow Zone Of S P Waves Crust Core Mantle Earth S Crust Youtube

Q Tbn 3aand9gcqq14sowink5sybs9 Eublkvwth0b7yx3qxra Usqp Cau

Seismic Waves As Probes Solid Earth Spu30x Courseware Edx Earth Science Lessons Seismic Wave Earth Science
Seismic Shadow Zones S Wave Shadow Zone Incorporated Research Institutions For Seismology

Evidence For Earth S Layers 8th Grade Science

Seismic Waves Generated By Earthquakes Examined Britannica

Shake Bake

How We Know About The Earth S Core Video Khan Academy
Seismic Study Of Earth S Interior Learning Geology

Earthquakes Earth S Interior

Geologic Fundamentals Of Geothermal Energy
Http Www Soest Hawaii Edu Gg Faculty Popp Oct07 Ch 12 Pdf

Seismic Shadow Zones S Wave Shadow Zone Incorporated Research Institutions For Seismology

Summing Up Zanichelli Online Per La Scuola

Seismic Waves Read Earth Science Ck 12 Foundation
How Earthquake Occurs And What Causes It Seismic Waves P And S Waves Youtube

Secondary Wave Seismology Britannica
Shadow Zone Wikipedia

Seismic Waves Read Earth Science Ck 12 Foundation
Seismic Waves Shadow Zone Of P Waves And S Waves Pmf Ias

Discovering Diamonds Select Topics

Four Types Of Seismic Waves Specifications Of All Types Of Seismic Waves
Greg Durocher Excellent Rollover Showing Various Seismic Wave Paths Through Earth T Co Nnpz0padxq Via Iris Epo Geology Earthquakes T Co Emakpvuuna

Seismic Shadow Zone Definition Overview Study Com
Seimic Waves And Earth S Interior
Seismic Waves Earth Science

Seismic Shadow Zones Introduction To P S Wave Shadow Zones Educational Youtube
Q Tbn 3aand9gcqiy1auiaz3uq6lxiipq5arhdo 5dqhjqcefsspvgdz3q 1aqay Usqp Cau

Section 9 2 Define Seismic Waves And Focus Ppt Download

Earth S Interior Earth Science

Chapter 8 Vocab Quizlet Flashcards Quizlet
Thread By Iris Epo Seismic Shadow Zone How Do P S Waves Give Evidence For A Liquid Outer Core Thread Iris Edu Hq Inclass Ani Earthquake Seismology Data
Seismology And Earthquakes
Waves As Probes
What Causes Earthquakes British Geological Survey
Seismic Phases S Wave Shadow Zone Youtube

Refraction And The Shadow Zone Definition Of Refraction The Change In Direction Of A Wave Due To Changes In Its Velocity As It Passes From One Medium Ppt Download
The Earth S Interior

Define Shadow Zone 1 Marks Brainly In
Earthquakes
Seismic Shadow Zones S Wave Shadow Zone Incorporated Research Institutions For Seismology



