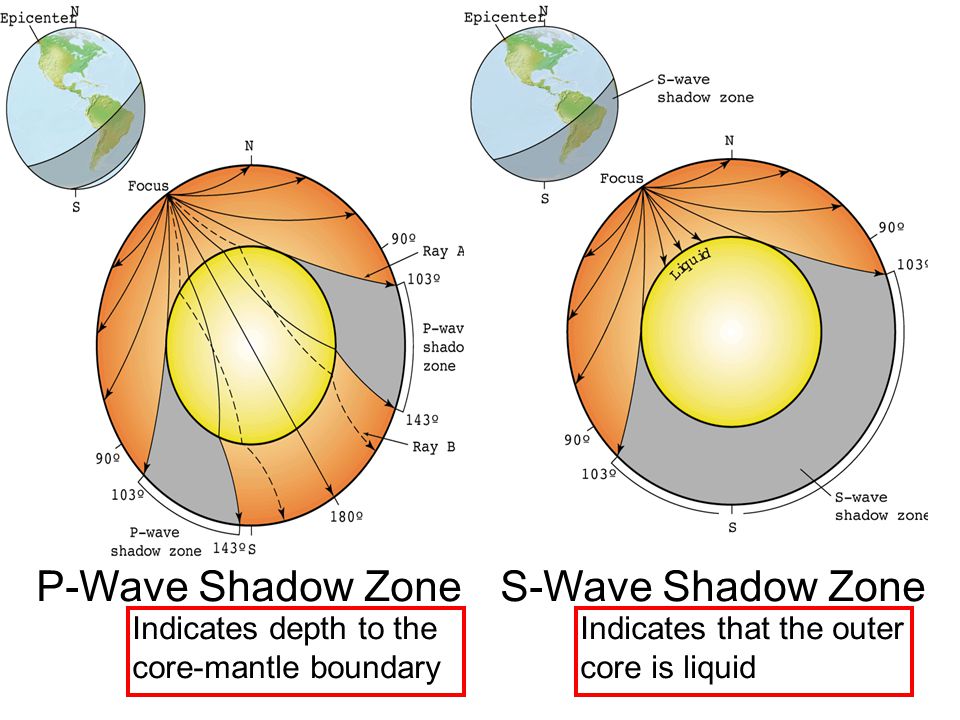
S Wave Shadow Zone Vs P Wave Shadow Zone

A Teachable Moment M6 2 Japan Texas Educational Seismic Project
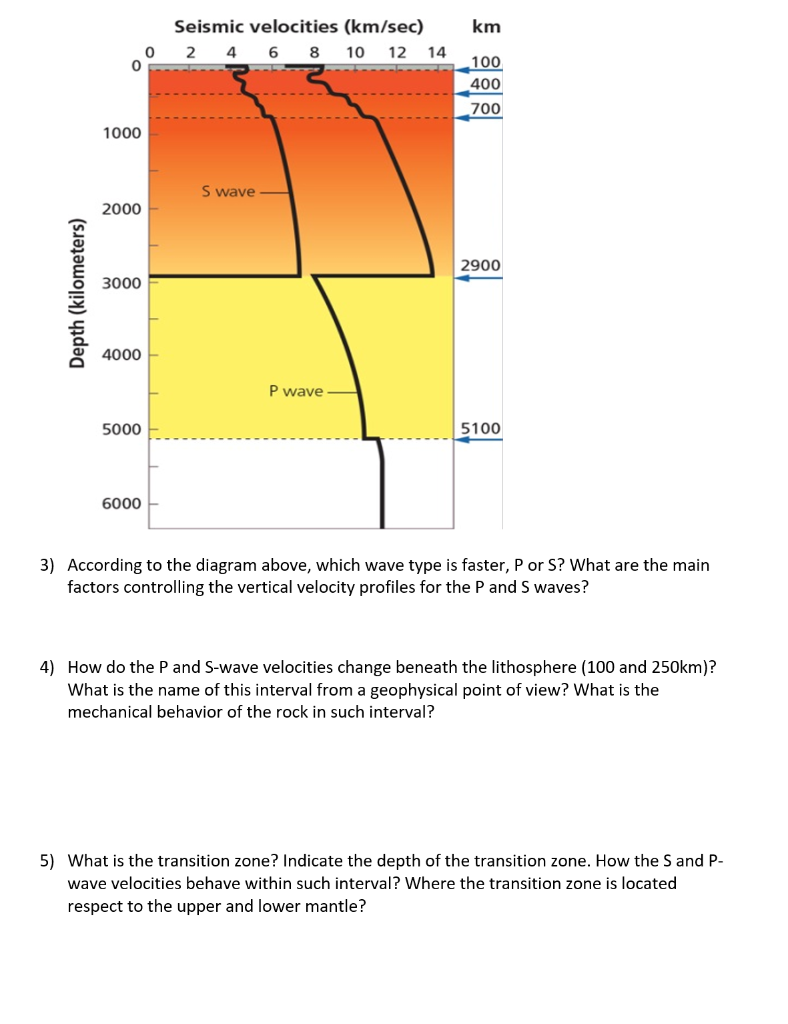
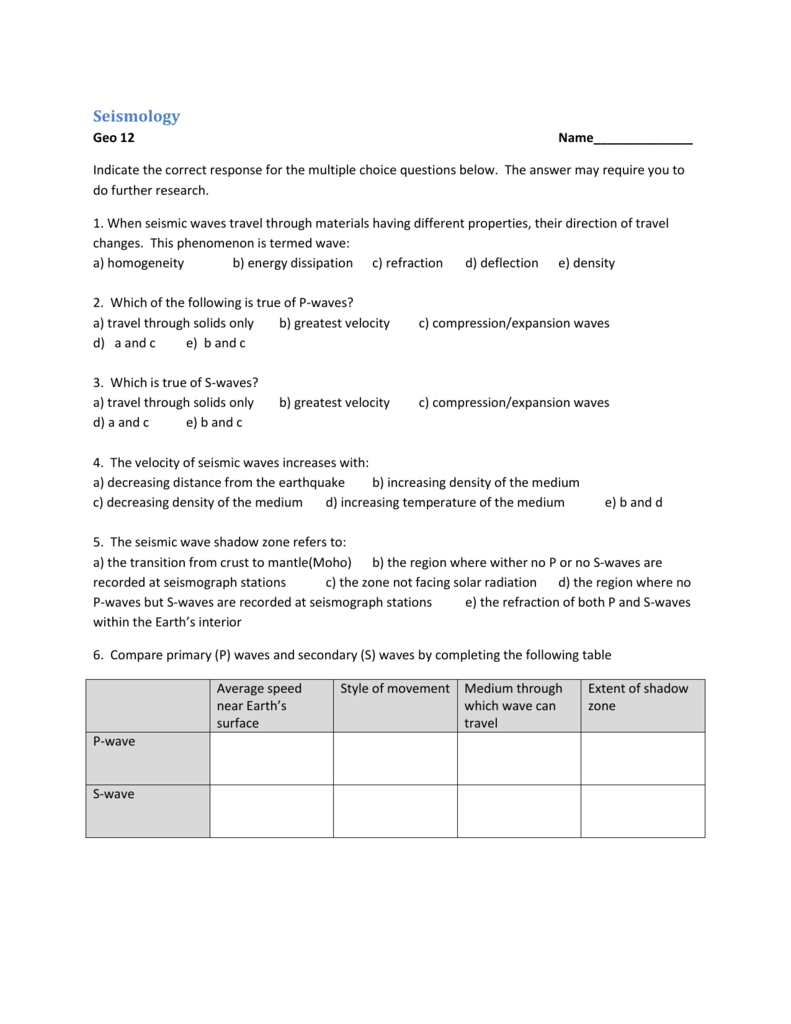
Seismic Waves

9 1 Understanding Earth Through Seismology Physical Geology

Tectonics Lecture 3 Internal Composition Of Earth Flashcards Quizlet
Seismic Shadow Zones S Wave Shadow Zone Incorporated Research Institutions For Seismology

Earthquakes And The Interior Earthquakes Are Definitely A Geologic Hazard For People Living In Earthquake Regions But The Seismic Waves Generated By Ppt Download
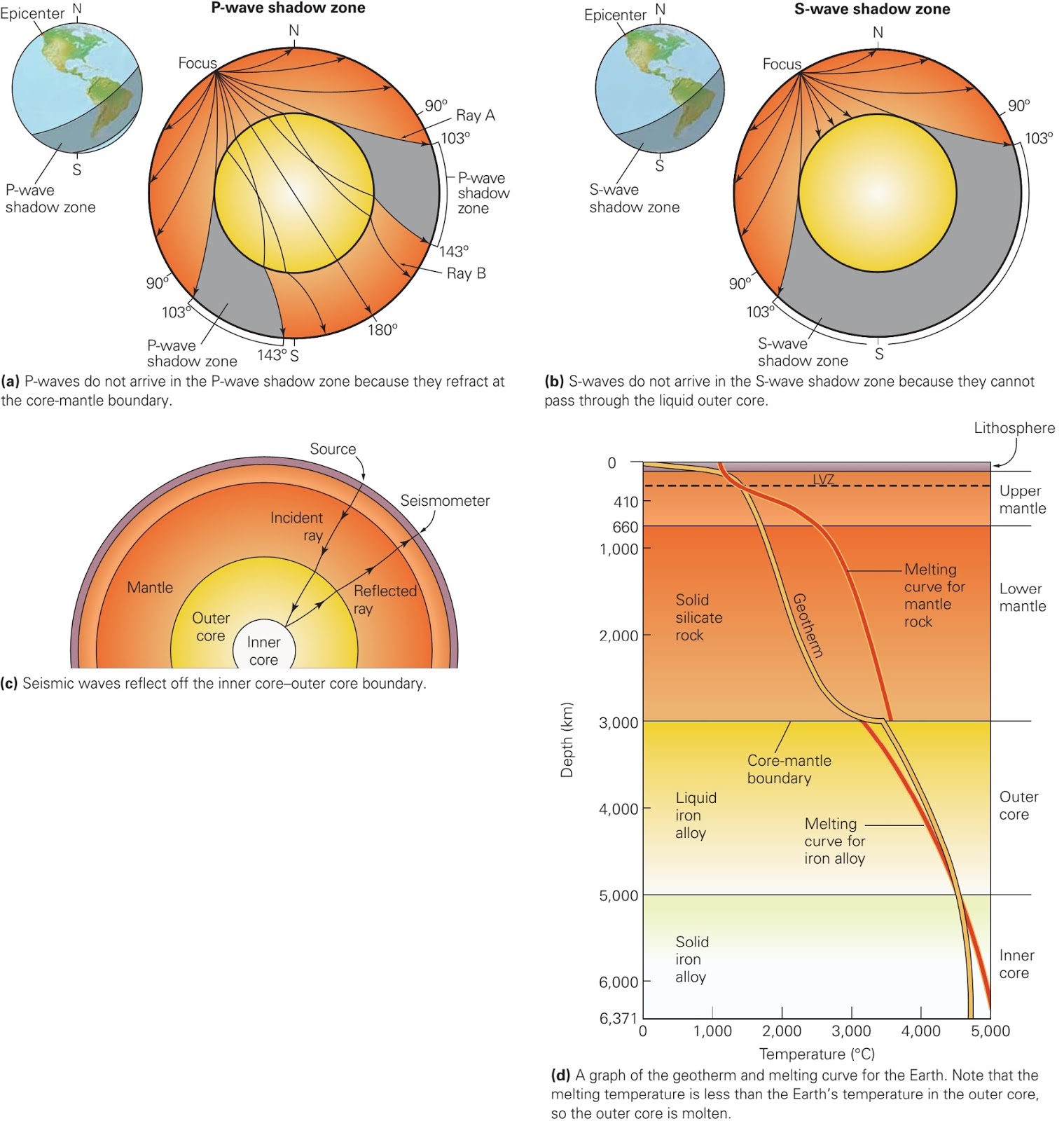
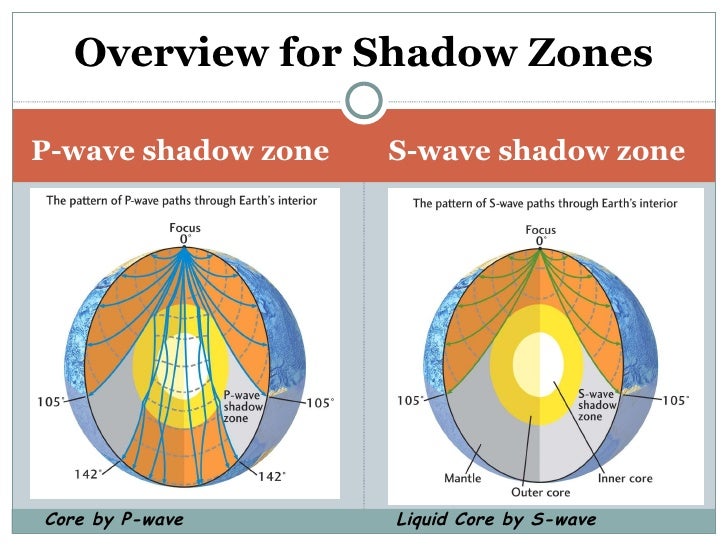
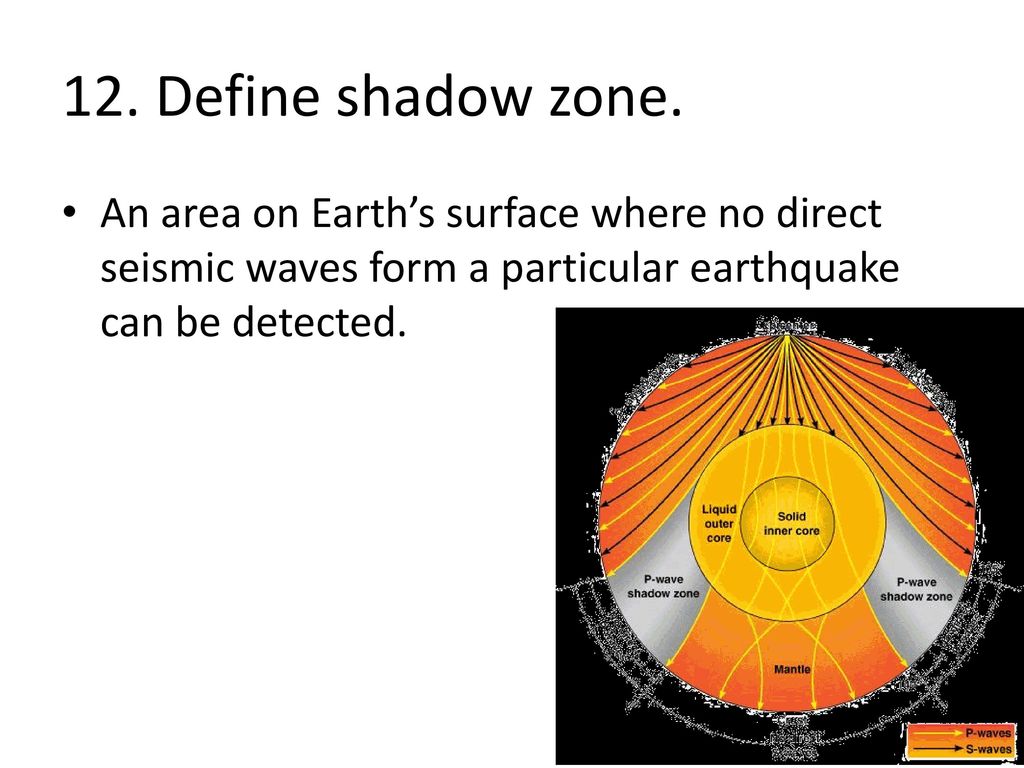
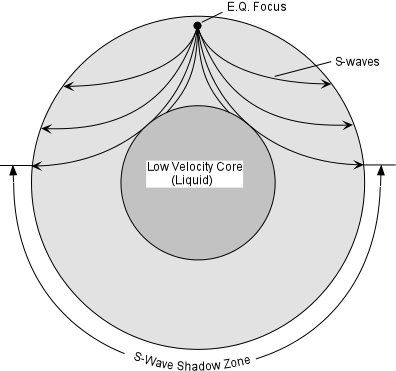
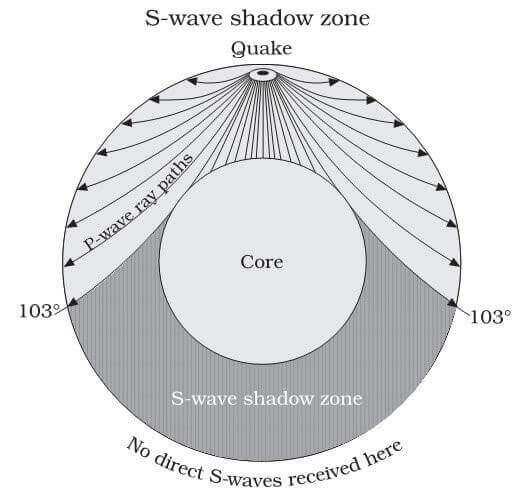
S-waves shadow zone means the area of the Earth from angular distances.
S wave shadow zone vs p wave shadow zone. P waves travel much faster than S waves so they reach the core faster. The entire zone beyond 103° does not receive S-waves, and hence this zone is identified as the shadow zone of S-waves. S wave shadow zone John Harrison.
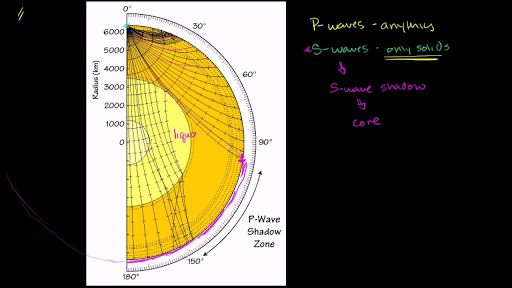
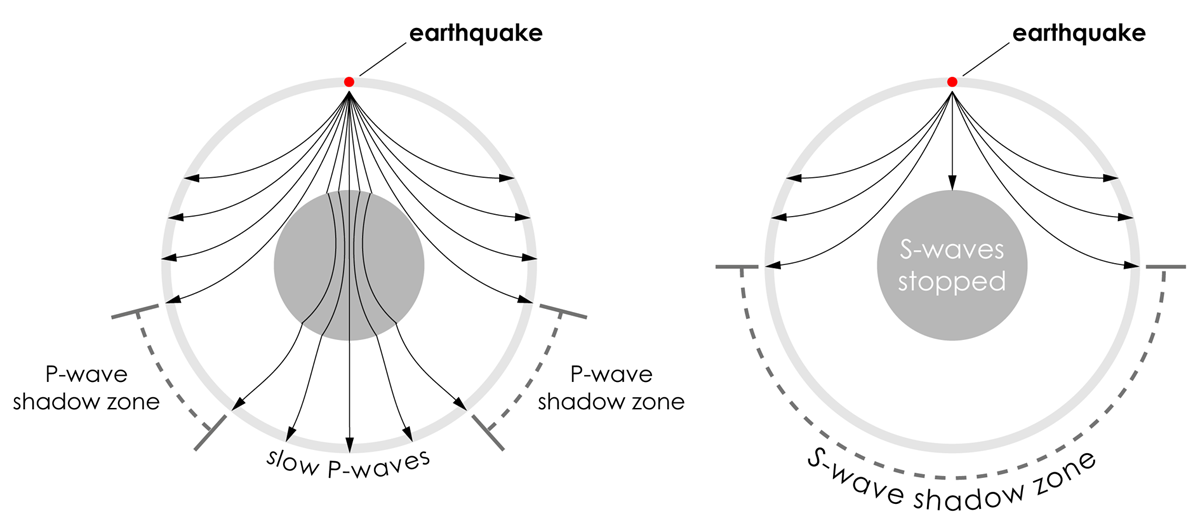
How can we use P and S wave shadow zones to conclusively prove that Earth's outer core is molten?. The shadow zone results from S waves being stopped entirely by the liquid core and P waves being bent (refracted) by the liquid core. A region of the subsurface from which seismic reflections cannot be detected because their ray-paths do not emerge to the surface.
Depending on the type of wave the size of the shadow zone can vary. This means that once these waves hit the liquid outer core of Earth, P-waves are refracted and S-waves are stopped. Seismic shadow zones are areas away from the epicenter of an earthquake that seismic waves are blocked or refracted away from.
A) and b) e) a) and c) 43 – The Richter scale classifies an earthquake according to its _____ which is a. The S-wave Shadow Zone Is Evidence That:. The fastest of these are primary, or "P," waves.
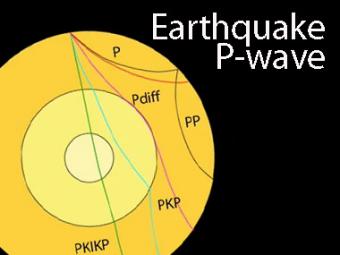
They can travel through the outer core, but change direction slightly, causing a p-waves shadow zone. The P-wave shadow zone can be explained by the refraction of P-waves at the ---core-mantle boundary. When a P-wave strikes the boundary of molten and solid cores at an oblique angle, S-waves will form and propagate in the solid medium.
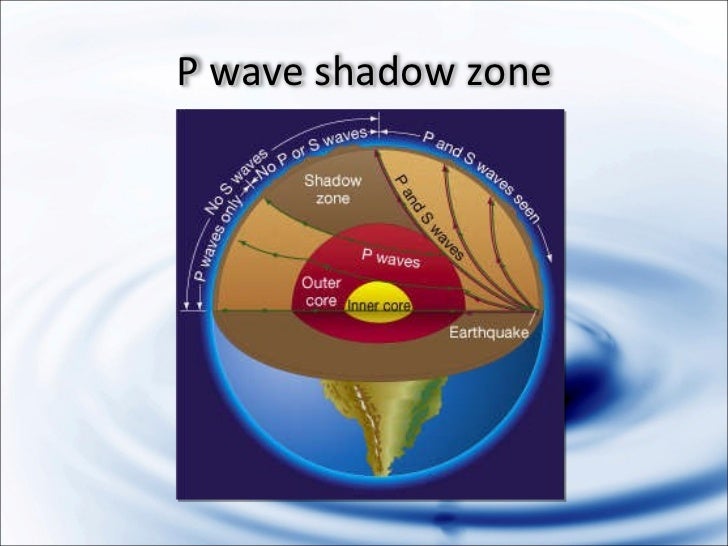
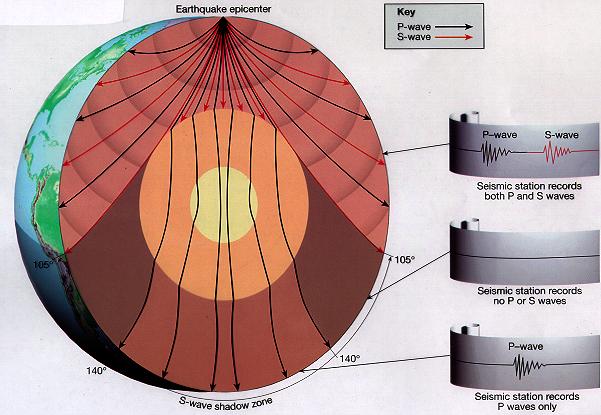
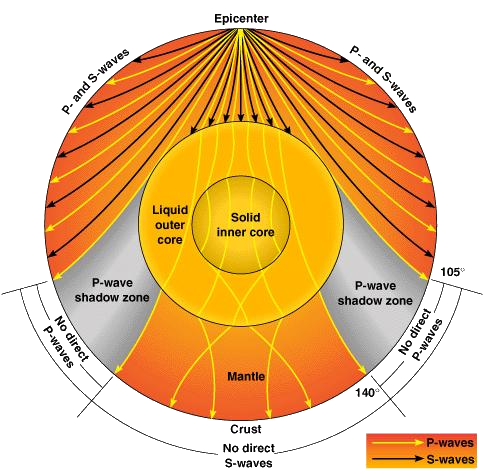
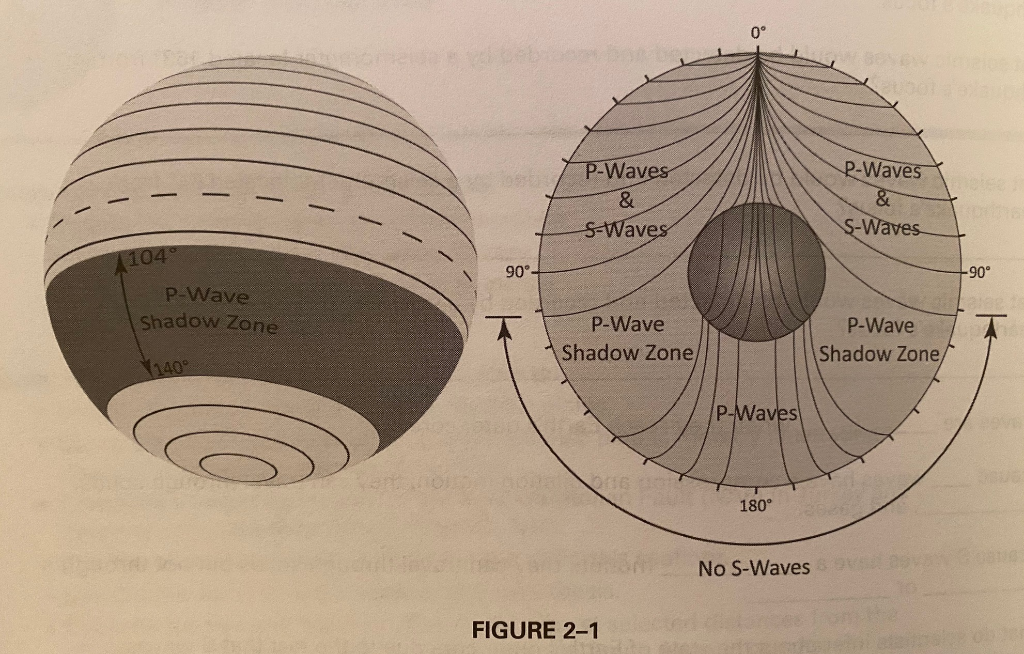
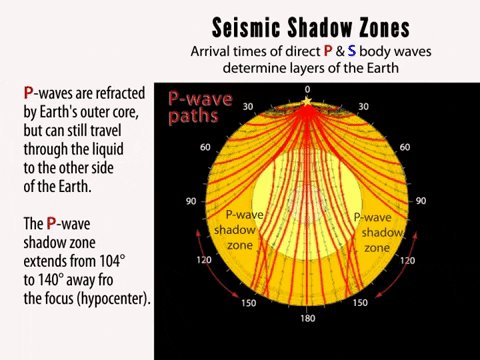
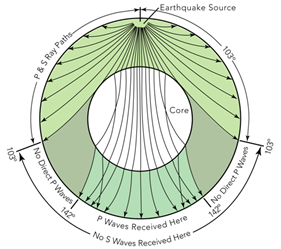
P waves are refracted by the liquid outer core and are not detected between 104° and 140° S waves cannot pass through the liquid outer core and are not detected beyond 104°. The s-waves shadow zone indicate the outer core is liquid. The --- is the transition zone at the core-mantle boundary.
2) P-waves are refracted and S-waves are absorbed by the. There are 2 different types of shadow zones (areas where these waves relative to the epicenter of the Earthquake. The crust-mantle boundary the outer core the lower mantle the inner core.
P waves are known as. The shadow zone results from S waves being stopped entirely by the liquid core and P wavesbeing bent (refracted) by the liquid core. Reflection at the mantle-core boundary directs the P waves toward a different area.
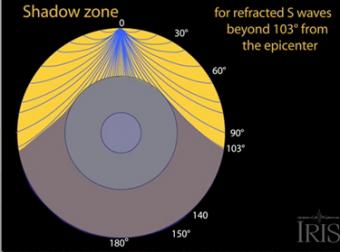
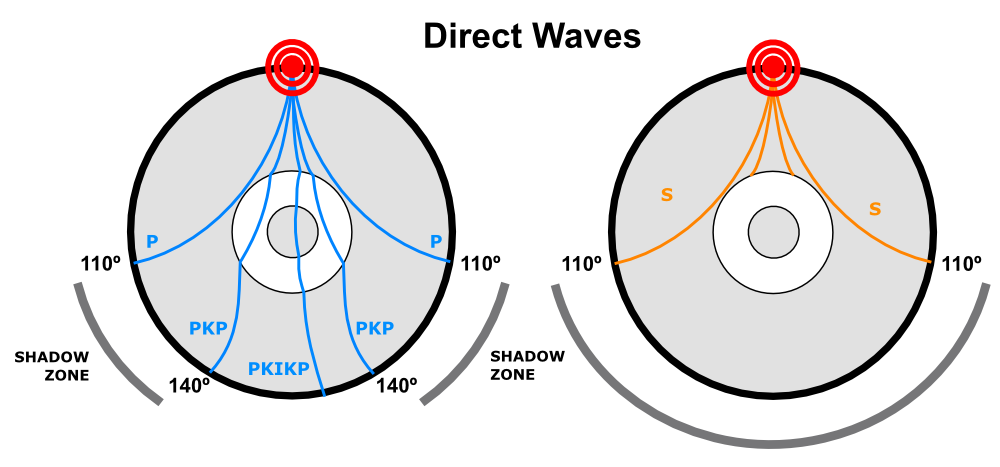
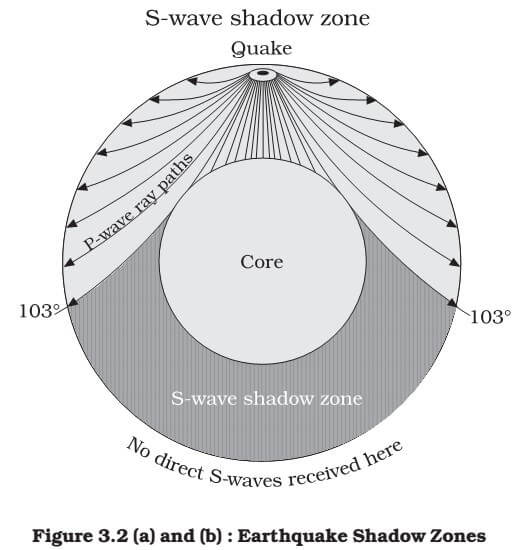
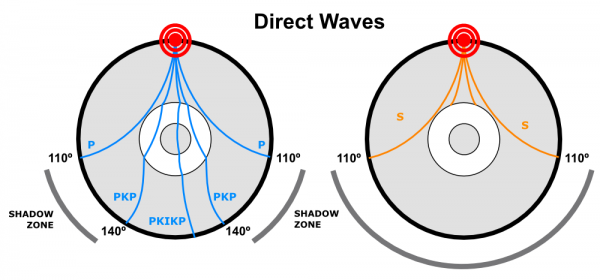
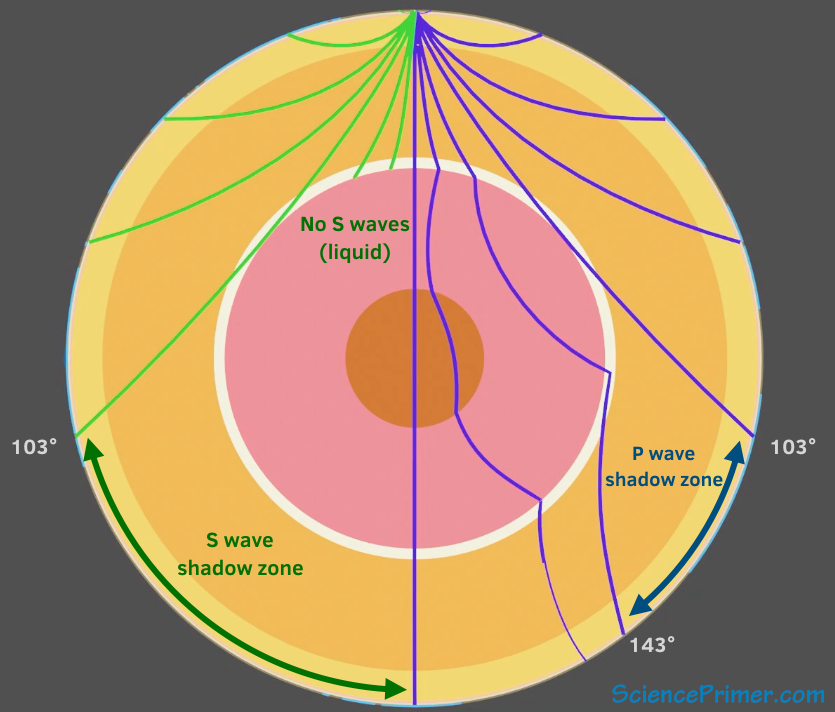
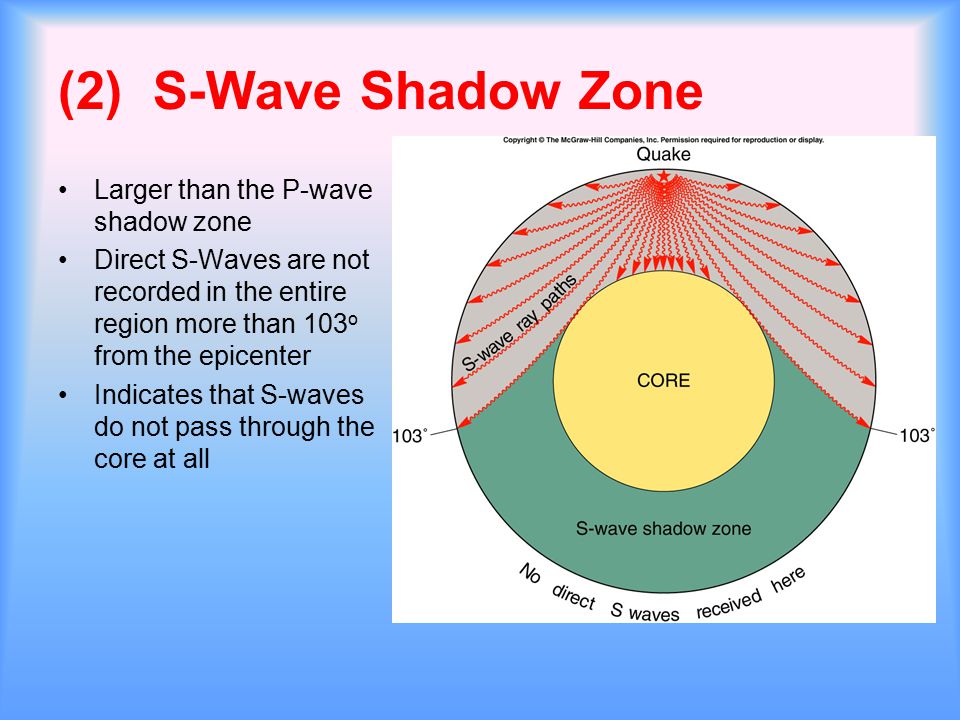
S waves can only travel through solids, and as a result do not travel through the liquid core of. It Is A Narrow Band That Lies 103ºto 143° From An Earthquake's Epicenter Where S-waves, But Not P-waves, Are Measured At Seismometers. S-waves cannot travel through water only solids.
Iron-nickel meteorites are an important source of information regarding the composition of Earth's ---core. Thus the shadow zone is where the S-waves stop. The P-wave shadow zone occurs for all of the following reasons the difference in rigidity between the mantle and core changes the speed of P waves.
What is a P-wave shadow zone?. The P-wave refract due to phase changes of seismic waves through different rocks in the Earth, increasing or decreasing the velocity. In shadow zone, seismograph does not record signals.
The S-wave shadow zone is a angle past 105 degrees, measured from the focus, that the S waves cannot exceed because they cannot travel through the Earth's liquid region core. The P-wave shadow zone is the area inside the earth where p waves can’t travel through because of refraction of seismic waves in the mantle and core. All are shear waves that tra.
Why is there a P-wave shadow zone?. D) a and b e) b and c 42. There are 2 different types of shadow zones (areas where these waves relative to the epicenter of the Earthquake.
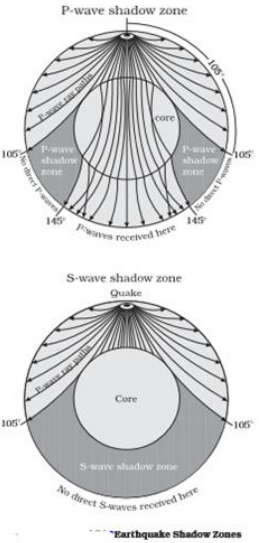
S-waves on the other hand will completely stop and dissipate once they hit liquids. The P-wave shadow zone is 105. The shadow zone is the area of the earth from angular distances of 104 to 140 degrees from a given earthquake that does not receive any direct P waves.
In contrast, S-waves do not travel through liquids. At larger distances, some P waves that travel through the liquid core would arrive, but still no S waves. What does the S wave shadow zone tell us?.
An S-wave shadow zone is produced when the S-waves hit water. Answered Sep 13, 16 by Abby99. The slowest body waves are secondary, or "S" waves.
To pass the quiz, an understanding of S- and P-wave shadow zones is necessary as well. The Earth has to have a molten, fluid core to explain the lack of S waves in the shadow zone, and the bending of P waves to form their shadow zone. Thanks Welcome to Sciemce, where you can.
A zone over the Earth's surface in which P-waves and/or S-waves generated by an earthquake are detected only weakly, or are absent, because of refraction within the various layers deep within the Earth, and especially in association with the Earth. A) the Earth’s inner core is solid. Both P and S waves are absorbed by the Earth's outer core HELP MEEEE.
The p wave shadow zone is caused by the refraction of the p waves as they travel through the earth from one medium to another. The P-wave shadow zone is 105. When an s-waves shadow zone is formed as seismic waves travel through the Earth's body.
Your browser does not support the video tag. This quiz/worksheet combination will test your knowledge of seismic shadow zones. As an earthquake warning.
Carefully the following Depth vs. That means there will be no any form of elastic waves or called p-waves. The area beyond 105 degrees distance forms a shadow zone.
Unsubscribe from John Harrison?. Www.iris.edu/earthquake for more animations. About This Quiz & Worksheet.
The shadow zone is the area of the earth from angular distances of 104 to 140 degrees from a given earthquake that does not receive any direct P waves. When earthquakes occur, they produce primary and secondary waves (called compression and shear waves sometimes). These compressional waves move faster in dense rock and slower in fluids.
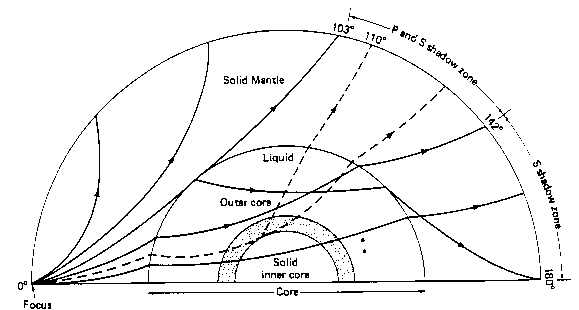
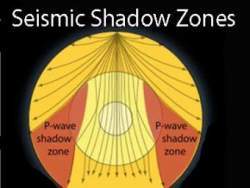
It Is Very Hot Near The Core The Inner Core Is Solid The Outer Core Is Composed Of Iron And Nickel Oxides The Outer Core Is Liquid The Distinction Between The Crust And The Mantle Is Primarily On The Basis Of A Difference In _____;. The shadow zone of a P-wave exists from 105 to 143 degrees (epicentral distance). Why are there P waves or S waves received in the P wave shadow zone?.
This shows how P waves travel through so. 1) Sketch and describe P- and S-wave shadow zones. P waves are absobed and S wave are refracted by the Earth's outer core B.
When an s. 1) P-waves are absorbed and S-waves are refracted by the earth' outer core. As a result, there is a P-wave " shadow zone " between 103° and 142° from the earthquake's focus, where the initial P-waves are not registered on seismometers.
41 – An S-wave shadow zone exists because _____. Seismic shadowing occurs on the opposite side of the Earth from the earthquake epicenter because the planet's liquid outer core refracts the longitudinal or compressional (P-waves) while it absorbs the transverse or shear waves (S-waves. An S wave is a transverse wave and travels slower than a P wave, thus arriving after the P wave.
B) The Earth’s outer core is liquid. Seismic shadow zones have taught us much about the inside of the earth. The shadow zone of an earthquake is usually located 100-150 degrees from the epicentre.
Label the lithosphere, lower velocity zone, asthenosphere, upper mantle, transition zone, lower mantle, outer core and inner core. The S wave shadow zone occurs because S waves do not pass through liquids and part of Earth's core is liquid. S waves are absobed and P wave are refracted by the Earth's outer core C.
The S wave shadow zone is caused by the _____. The seismic shadow zone is the rea of the Earth's surface where seismographs cannot detect an earthquake after the waves have passed through the earth;. Visualization of S and P Wave Shadow Zones - Duration:.
Seismic shadow zones have taught us much about the inside of the earth. The shadow zone of P-waves appears as a band around the earth between 103° and 142° away from the epicentre. When an S-wave hits the core, it stops since the core is molten hot lava.
Shadowzones are produced on the other sides of the planet due to waves being refracted or blocked by the liquid outer core of Earth. C) S-waves are only transmitted through solid media. Liquids, however, have zero rigidity, hence always making the S-wave velocity overall zero and as such S-waves lose all velocity when travelling through a liquid.
Because they are deflected by the earth's core, P waves are not seen in the so-called shadow-zone. False P-wave rays are most commonly reflected while S-wave rays are refracted. Part of the P wave is also reflected.
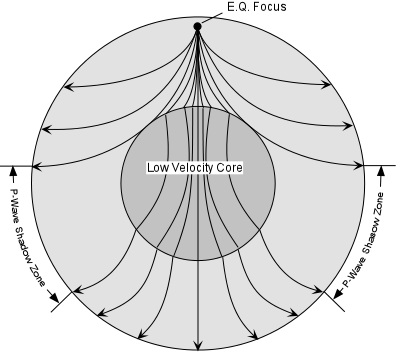
This shows how P waves travel through solids and liquids, but S waves are stopped by the liquid outer core. Both P and S waves are refracted by the Earth's outer core D. Epicenter N P-wave Shadow Zone Focus 90 103 P-wave Shadow Zone P-wave Shadow Zone 143° 90° 1030 180° P-wave Shadow Zone Choose One:.
This shadow zone has led geologists to a model of the Earth with a solid mantle. S-waves shadow zone means the area of the Earth from angular distances. For P-wave it is b/w 104-145 degress.These earthquake waves exhibit same properties as other waves like reflection, refraction etc.As core has.
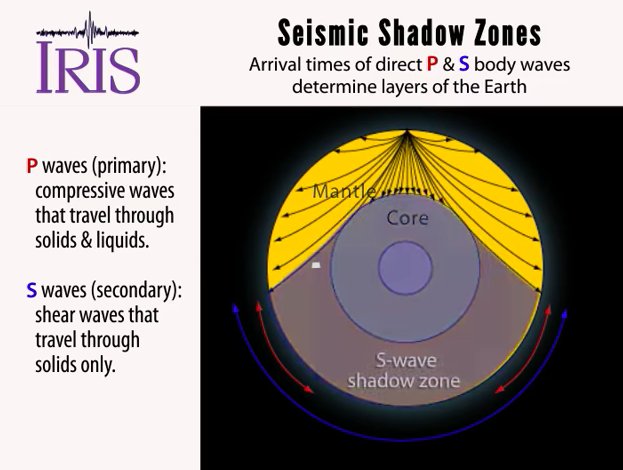
Where P waves suddenly disappear from seismographs, they refract off earth's core, used to calculate size/shape of core, suggests liquid outer core and solid inner core since S waves do not move through liquid and their shadow zone is much larger, this tells us that the core must be liquid/acts like liquid. The S wave shadow zone is the area of the Earth’s surface where S waves are not detected following an earthquake. S waves move rock particles up and down, or side-to-side--perpendicular to the direction that the wave is traveling in (the direction of wave propagation).
Unlike P-waves, S-waves cannot travel through the molten outer core of the Earth, and this causes a shadow zone for S-waves opposite to their origin. This is caused by P waves meeting the liquid outer core and being refracted. This means that once these waves hit the liquid outer core of Earth, P-waves are refracted and S-waves are stopped.
This video is unavailable. S-waves on the other hand will completely stop and dissipate once they hit liquids. What property(ies) of rock determines the seismic wave velocity through it?.
It is this property of S waves that led seismologists to conclude that the Earth's outer core is a liquid. This lesson will cover seismic shadow zones and discuss what they. As a result, there is a P-wave "shadow zone" between 103° and 142° from the earthquake's focus, where the initial P-waves are not registered on seismometers.
P waves travel more slowly in the outer core than in the lower mantle Liquids do not transmit S waves. Thus, their speed and direction change. A P-wave shadow zone is produced when the P-waves have traveled through the whole earth.
No P-waves or S-waves are received in the shadow zone because;. The P wave shadow zone occurs because P waves slow down and get refracted when they pass through the part of Earth's core that is liquid. Www.iris.edu/hq/programs/education_and_outreach/animations Animation addresses 3 common variations of S-type seismic body waves.
P-waves, however, are only partially dependent on rigidity and as such still maintain some velocity (if greatly reduced) when travelling through a liquid. This observation led to the discovery of the liquid outer core. The S-wave shadow zone extends from _____ to 180 o angular distance from the earthquake focus on one side and from.
Since s waves cannot travel through the. The Distinction Between The Lithosphere And The Asthenosphere Is Primarily.
Earthquakes

How Seismic Waves Tell Us About Earth S Core Capitol Hill Science 8
Solved 1 Sketch And Describe P And S Wave Shadow Zones Chegg Com
How We Know About The Earth S Core Video Khan Academy

Layered Structure Earth Crust Mantle Metal Inner Outer Core Iron Nickel S P Earthquake Waves Shadow Zones Geology Earth Gcse Science Revision Notes

My Favorite Demonstration The P Wave Shadow Zone Shedding Light On The Concept
Escweb Wr Usgs Gov Share Mooney Sril Ii2 Pdf
Direct Waves Highly Allochthonous

Seismic Waves
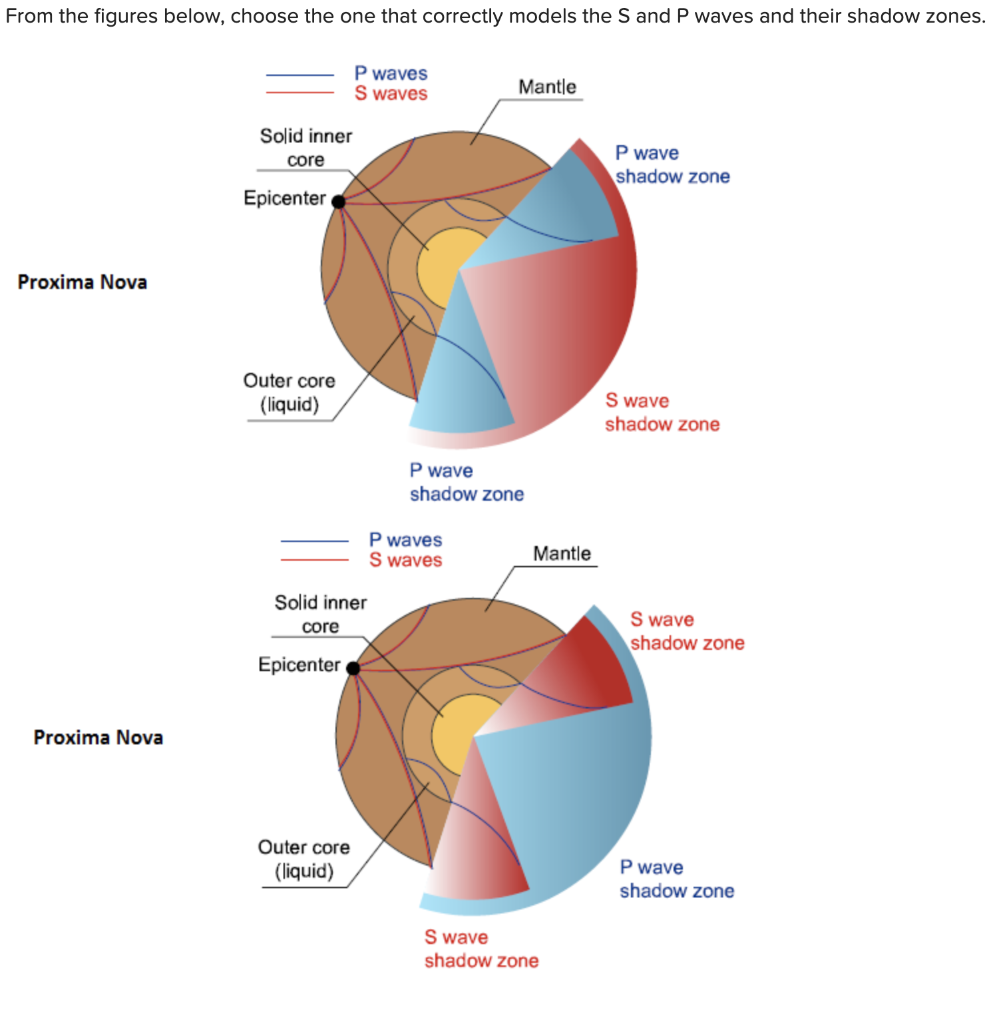
Solved Click To Select V Is The Correct Model Of The S Chegg Com
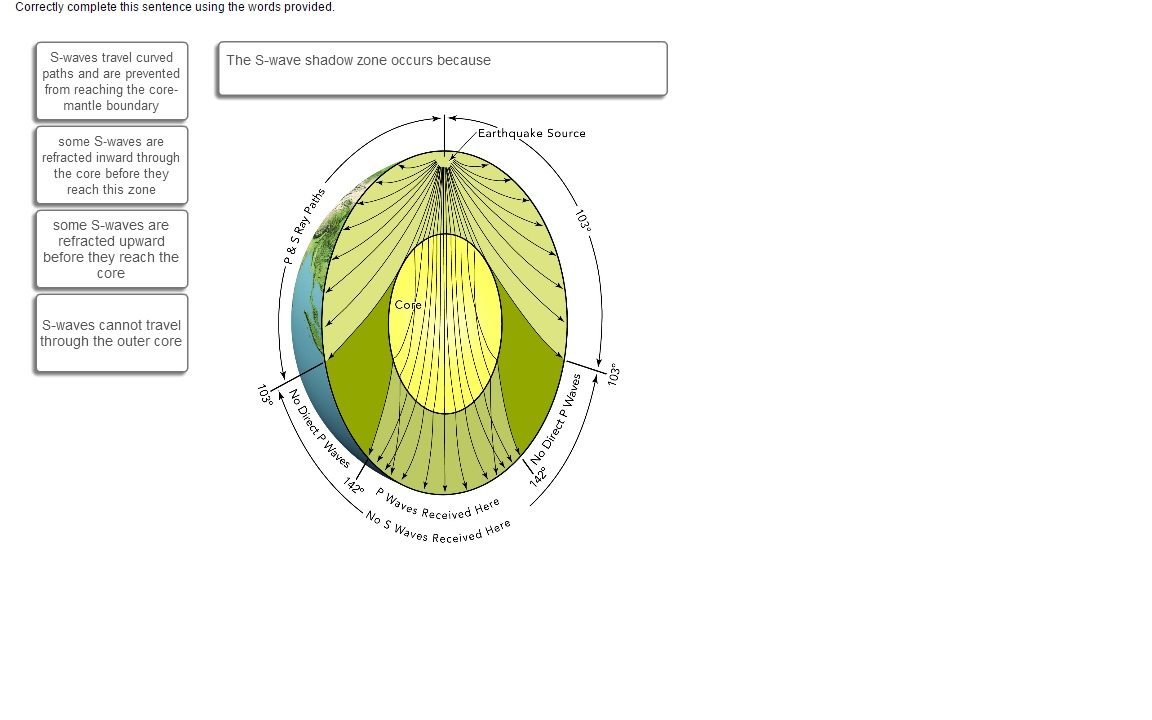
Solved Correctly Complete This Sentence Using The Words P Chegg Com

Velocity Of Seismic Waves At Different Depths Google Search Earth Layers Earth Science Geology
Earthquakes
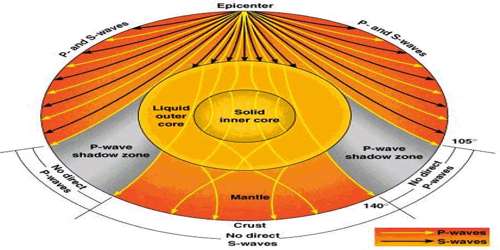
Emergence Of Shadow Zone Of Earthquake Qs Study
D32ogoqmya1dw8 Cloudfront Net Files Angle Educational Materials Activities Human Wave Modeling P Pdf

March 29 1936 Notes On Earth S Inner Core Earth Magazine
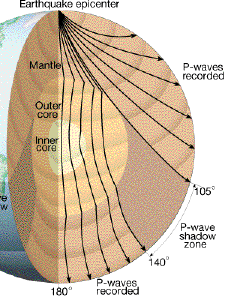
Multiple Choice
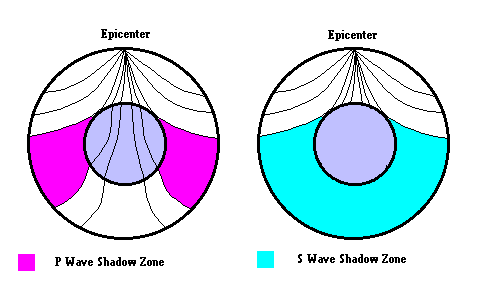
Waves As Probes
What Is A Shadow Zone During An Earthquake Quora

Ppt Chapter 7 Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id

01 Chapter Earthquake

Seismic Waves Shadow Zone Of P Waves And S Waves Pmf Ias
Seismic Profiles Of Earth S Interior Ppt Video Online Download

Earthquakes Happen Every Day Every Hour Somewhere In The World 95 Of Seismicity In Hawaii Is Due To Volcanism Ppt Download

Shadow Zones Mechanical Wave Earth Science Outer Core
Earthquake Waves Body And Surface Waves And Concept Of Shadow Zone Issues And Analysis Abhipedia Powered By Abhimanu Ias

Seismic Waves As Probes Solid Earth Spu30x Courseware Edx Earth Science Lessons Seismic Wave Earth Science
Http Www3 Nd Edu Cneal Planetearth Chapt 10 Marshak Pdf
Ocean 540 Geologic Overview
3 2 Seismology
Seismic Study Of Earth S Interior Learning Geology

Introduction To Earthquakes Vocabulary Seismic Waves Help Reveal The Structure Of Earth S Interior Diagram Quizlet

Evidence For Earth S Layers 8th Grade Science
Q Tbn 3aand9gctv397au8bajkuvy8scub8qu2zlodynbq58gqadl2c Usqp Cau
Oncel Akademi Solid Earth Geophysics
Smart Study Zone Types Of Earthquake Seismic Waves In English
Seismic Waves Earth S Structure
Http Www3 Nd Edu Cneal Planetearth Chapt 10 Marshak Pdf

9 1 Understanding Earth Through Seismology Physical Geology

Which Country Has A Shadow Zone Area Where Earthquake Does Not Occur Quora

Evidence For Earth S Layers 8th Grade Science
Solved Could You Also Explain How You Navigated The Figur Chegg Com

1 Sketch And Describe P And S Wave Shadow Zones Chegg Com
1
We Have A Seismometer In Our Basement Highly Allochthonous

Earth Tests Ch12

Unacademy For Upsc Geography Series 4
Q Tbn 3aand9gcrawr S39vofkg1f8eemjggywsjlg1qanpcnkaymr Iqudfbmw7 Usqp Cau
Thread By Iris Epo Seismic Shadow Zone How Do P S Waves Give Evidence For A Liquid Outer Core Thread Iris Edu Hq Inclass Ani Earthquake Seismology Data

Shadow Zone Activity
Www E Education Psu Edu Earth106 Sites Www E Education Psu Edu Earth106 Files Earth106 Lect10 12 Pdf
What Is A Shadow Zone During An Earthquake Quora

A Simple Diagram That Illustrates The Shadow Zone For An Assumed Download Scientific Diagram
Iris Earthquake Sci Video 00 02 00 Introduction To Seismic Shadow Zones Seismic Shadow Zones Have Taught Us Much About The Inside Of The Earth This Shows How P Waves

Earth S Interior
Handout 1 Standard 2 1 A B And C Ppt Download
Q Tbn 3aand9gcqiy1auiaz3uq6lxiipq5arhdo 5dqhjqcefsspvgdz3q 1aqay Usqp Cau
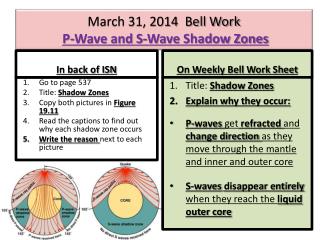
Ppt March 31 14 Bell Work P Wave And S Wave Shadow Zones Powerpoint Presentation Id

Chapter 8 Flashcards Quizlet

Earthquakes Ppt

Earth Sci Eq Flashcards Quizlet
Http Www Soest Hawaii Edu Oceanography Courses Html Ocn1 Instructors Ferron Ocn1 L5 Earth structure Pdf
How Earthquakes Show Us The Inside Of The Earth Science Primer

Seismic Shadow Zones Introduction To P S Wave Shadow Zones Educational Youtube

A Seismic Shadow Zone Best Ias Ukpsc Coaching In Dehradun
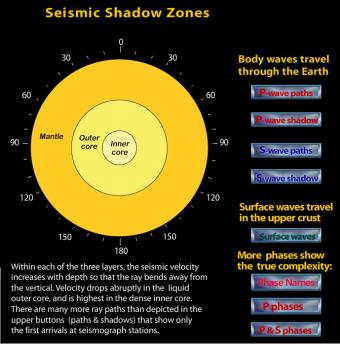
Shadow Zone Rollover Incorporated Research Institutions For Seismology

What Creates A Shadow Zone What Are The Ranges Of The Shadow Zones For S Waves And Homeworklib
Earthquakes

5 A Cross Section Of The Earth With Earthquake Wave Paths Defined And Download Scientific Diagram
How Do We Really Know What S Inside The Earth Imaging Earth S Interior With Seismic Waves Incorporated Research Institutions For Seismology
2
Seismic Shadow Zone Basic Introduction Incorporated Research Institutions For Seismology

Seismic Phases P Wave Shadow Zone Youtube

Seismic Waves Surface Waves Seismic Waves Are Shock Waves Given Off By Earthquakes There Are 2 Types 1 Body Waves Originate From The Focus F Travel Ppt Download

A Conceptual Magmatic Bodies Shown With Location Of S Wave Shadow Download Scientific Diagram
Geophysical Properties Ppt Video Online Download
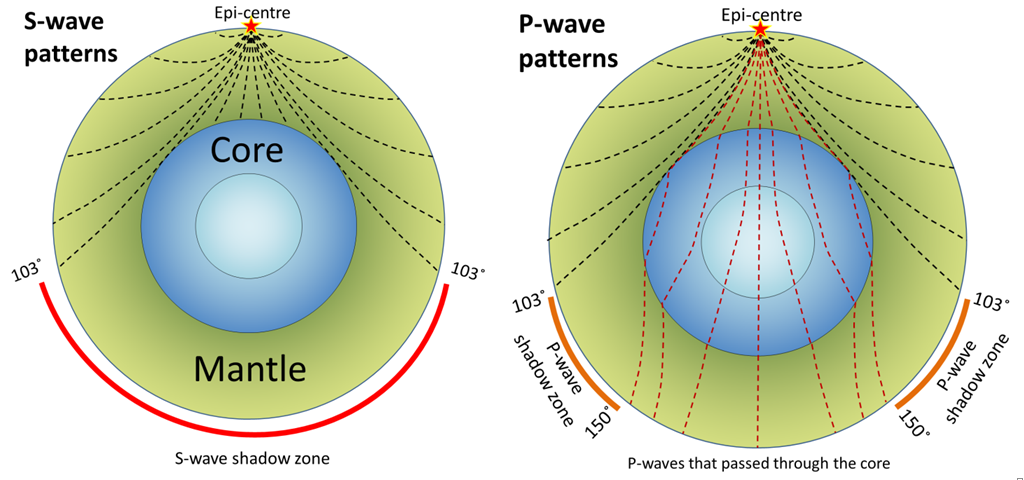
3 2 Imaging Earth S Interior Physical Geology First University Of Saskatchewan Edition

Multiple Choice Seismology Mantle Geology
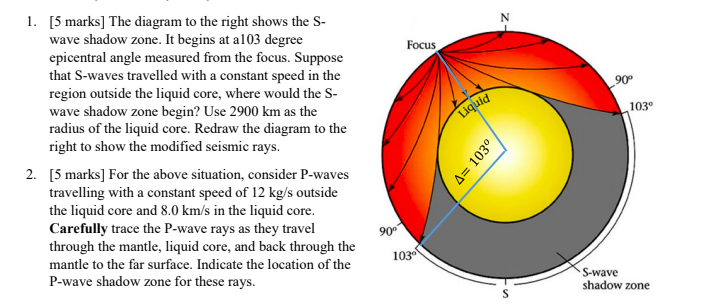
Focus 1 5 Marks The Diagram To The Right Shows Chegg Com

Shadow Zones Schoolworkhelper

Earthquakes
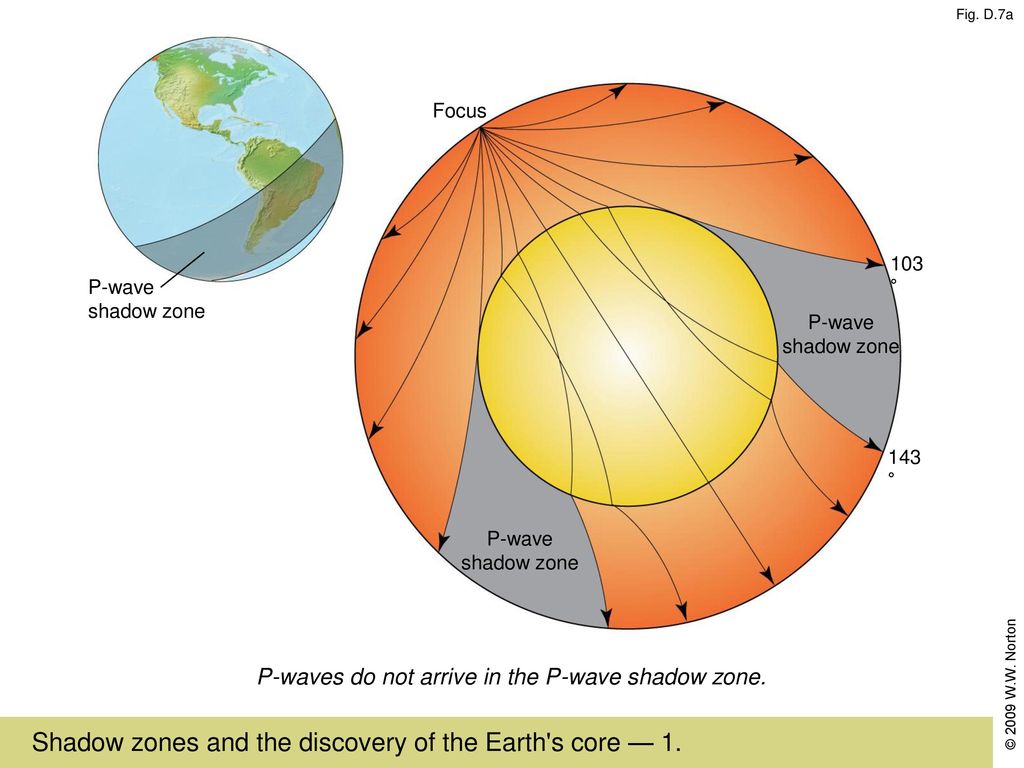
Seeing Inside The Earth Ppt Download

01 Chapter Earthquake
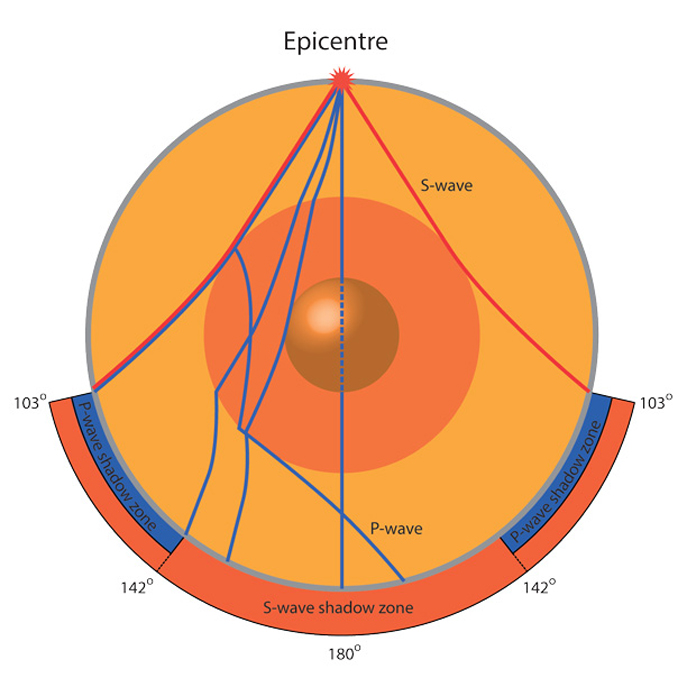
What Causes Earthquakes British Geological Survey

Why Are Seismic Waves Not Detected Within The Shadow Zone Quora

Earthquake Shadows Earth Science Ck 12 Plix Series

P Wave Wikipedia

How Do I Read A Seismogram
Seismic Waves Shadow Zone Of P Waves And S Waves Pmf Ias
Earth Structure Earth Science Visionlearning
Solved X00a0 The Cause Of The P Wave Shadow Zone Includes Chegg Com
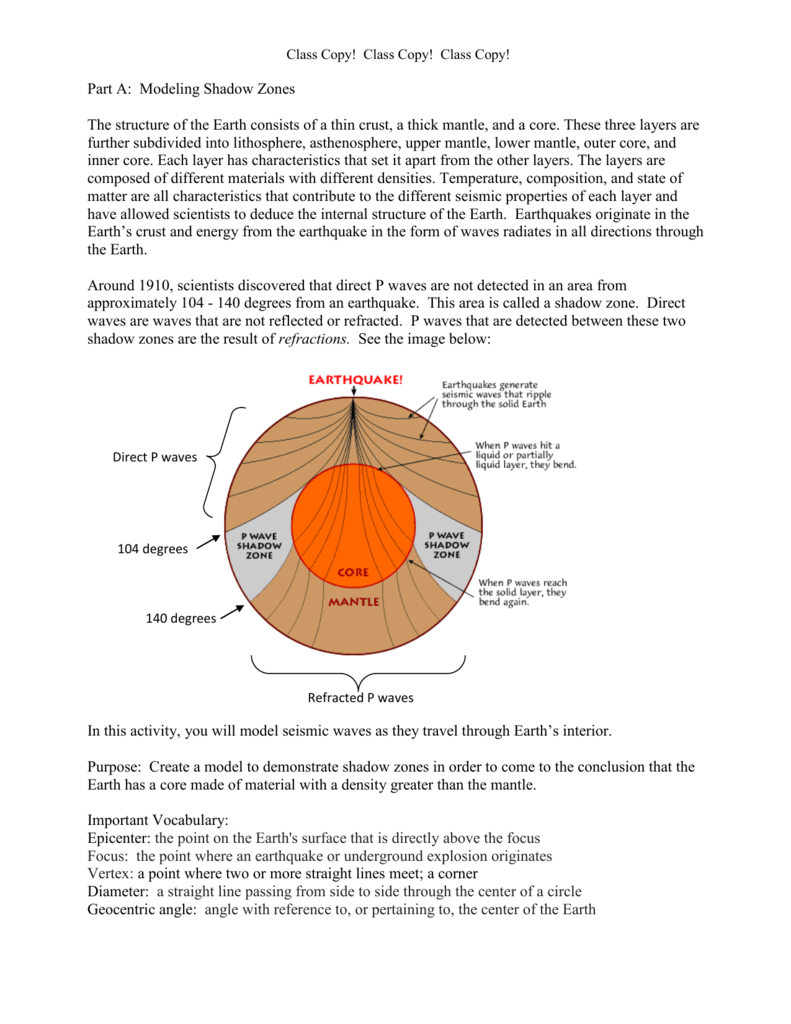
Modeling Shadow Zones And Earth Magnetic Field

Solved Problem Solving Module 12 Studying Earth S Intern Chegg Com

Layered Structure Earth Crust Mantle Metal Inner Outer Core Iron Nickel S P Earthquake Waves Shadow Zones Geology Earth Gcse Science Revision Notes

My Favorite Demonstration The P Wave Shadow Zone Shedding Light On The Concept
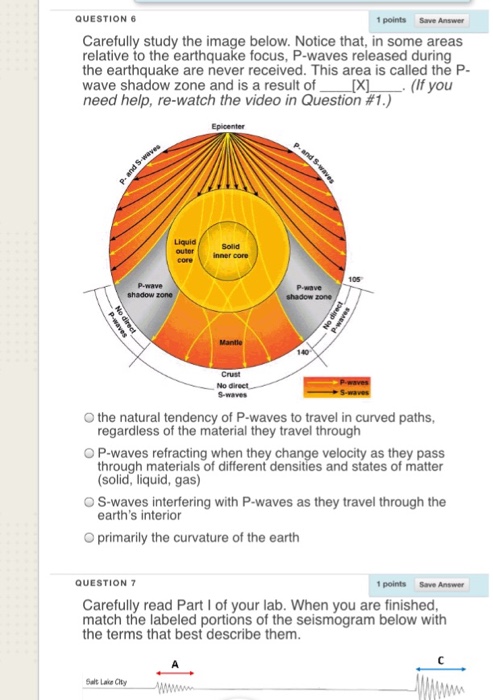
Solved Carefully Study The Image Below Notice That In S Chegg Com

Geol212 Planetary Geology

Seismicity And Earth S Interior Part I Chapter 18 Dynamic Earth Eric H Christiansen Ppt Download



